Faster Cryptococcus Melanization Increases Virulence in Experimental and Human Cryptococcosis
- PMID: 35448624
- PMCID: PMC9029458
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8040393
Faster Cryptococcus Melanization Increases Virulence in Experimental and Human Cryptococcosis
Abstract
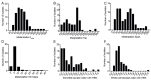
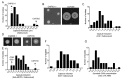
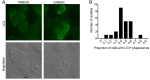
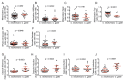
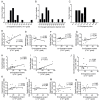
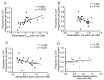
Cryptococcus spp. are human pathogens that cause 181,000 deaths per year. In this work, we systematically investigated the virulence attributes of Cryptococcus spp. clinical isolates and correlated them with patient data to better understand cryptococcosis. We collected 66 C. neoformans and 19 C. gattii clinical isolates and analyzed multiple virulence phenotypes and host-pathogen interaction outcomes. C. neoformans isolates tended to melanize faster and more intensely and produce thinner capsules in comparison with C. gattii. We also observed correlations that match previous studies, such as that between secreted laccase and disease outcome in patients. We measured Cryptococcus colony melanization kinetics, which followed a sigmoidal curve for most isolates, and showed that faster melanization correlated positively with LC3-associated phagocytosis evasion, virulence in Galleria mellonella and worse prognosis in humans. These results suggest that the speed of melanization, more than the total amount of melanin Cryptococcus spp. produces, is crucial for virulence.
Keywords: Cryptococcus neoformans; Galleria mellonella; LC3-associated phagocytosis; capsule; cryptococcosis; extracellular vesicles; melanin; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Kwon-Chung K.J., Bennett J.E., Wickes B.L., Meyer W., Cuomo C.A., Wollenburg K.R., Bicanic T.A., Castañeda E., Chang Y.C., Chen J., et al. The Case for Adopting the “Species Complex” Nomenclature for the Etiologic Agents of Cryptococcosis. mSphere. 2017;2:e00357-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00357-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perfect J.R., Dismukes W.E., Dromer F., Goldman D.L., Graybill J.R., Hamill R.J., Harrison T.S., Larsen R.A., Lortholary O., Nguyen M.-H., et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Cryptococcal Disease: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010;50:291–322. doi: 10.1086/649858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

