Dietary Patterns in Runners with Gastrointestinal Disorders
- PMID: 33572891
- PMCID: PMC7912258
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13020448
Dietary Patterns in Runners with Gastrointestinal Disorders
Abstract
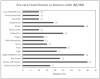
Individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and reflux frequently experience gastrointestinal symptoms (GIS), potentially enhanced by high-intensity running. Food avoidances, food choices, and GIS in runners with IBS/IBD (n = 53) and reflux (n = 37) were evaluated using a reliability and validity tested questionnaire. Comparisons to a control group of runners (n = 375) were made using a Fisher's Exact test. Runners with IBS/IBD experienced the greatest amount of exercise-induced GIS followed by those with reflux. Commonly reported GIS were stomach pain/cramps (77%; 53%), bloating (52%; 50%), intestinal pain/cramps (58%; 33%), and diarrhea (58%; 39%) in IBS/IBD and reflux groups respectively. In the pre-race meal, those with IBS/IBD frequently avoided milk products (53%), legumes (37%), and meat (31%); whereas, runners with reflux avoided milk (38%), meat (36%), and high-fibre foods (33%). When considering food choices pre-race, runners with IBS/IBD chose grains containing gluten (40%), high fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides and polyols (FODMAP) fruits (38%), and water (38%). Runners with reflux chose water (51%), grains containing gluten (37%), and eggs (31%). In conclusion, while many runners with IBS/IBD and reflux are avoiding trigger foods in their pre-race meals, they are also consuming potentially aggravating foods, suggesting nutrition advice may be warranted.
Keywords: dietary patterns; dietary restrictions; exercise-induced gastrointestinal symptoms; heartburn/reflux; inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); irritable bowel syndrome (IBS); runners; runner’s gut.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Hoogervorst D., van der Burg N., Versteegen J.J., Lambrechtse K.J., Redegeld M.I., Cornelissen L.A.J., Wardenaar F.C. Gastrointestinal complaints and correlations with self-reported macronutrient intake in independent groups of (ultra) marathon runners competing at different distances. Sports. 2019;7:1–18. doi: 10.3390/sports7060140. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources