Beinaglutide showed significant weight-loss benefit and effective glycaemic control for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in a real-world setting: a 3-month, multicentre, observational, retrospective, open-label study
- PMID: 31452921
- PMCID: PMC6700512
- DOI: 10.1002/osp4.342
Beinaglutide showed significant weight-loss benefit and effective glycaemic control for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in a real-world setting: a 3-month, multicentre, observational, retrospective, open-label study
Abstract
Aims: The purpose of this study was to examine the effectiveness of beinaglutide on body weight, glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), blood pressure and lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in a real-world setting in China.
Materials and methods: This was a multicentre, observational, retrospective, open-label study conducted in China. Data were collected from T2DM patients who started treatment with beinaglutide between 2017 and 2018.
Results: A total of 314 patients were included in the study. After 3 months of treatment with beinaglutide, there were significant reductions in body weight (-10.05 kg [95% confidence interval -9.29 to -10.80]), HbA1c (-2.87% [-2.62 to -3.11]), 2-h postprandial plasma glucose (-5.46 mmol L-1 [-4.96 to -5.95]) and fasting plasma glucose (-3.04 mmol L-1 [-2.78 to -3.31]) (all p < 0.0001). In addition, 84.96% and 72.18% of the patients achieved weight loss of ≥5% and ≥10%, respectively. Subgroup analyses showed that weight loss was significantly greater in patients with ≥28 kg m-2 of baseline body mass index and 0.60 mg of beinaglutide doses (p = 0.007 and p < 0.0001, respectively). HbA1c reductions were significantly greater in patients with ≥9.0% baseline HbA1c and in those administered 0.40-0.48 mg of beinaglutide doses (all p < 0.0001). Weight loss at 3 months was positively correlated with baseline BMI and the dose of beinaglutide. Positive determinants for HbA1c reduction after 3 months were baseline HbA1c and the dose of beinaglutide.
Conclusions: These observational results confirmed the benefits of beinaglutide in weight loss and glycaemic control and support the use of beinaglutide as an effective treatment for T2DM.
Keywords: Beinaglutide; GLP‐1; T2DM; obesity; weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that they have no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
Figures
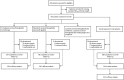
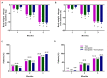
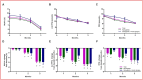
References
-
- Bunkenborg M. The uneven seepage of science: diabetes and biosociality in China. Health Place. 2016; 39: 212–218. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, et al. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013; 310: 948–959. - PubMed
-
- Tao L, Wang L, Yang X, Jiang X, Hua F. Recombinant human glucagon‐like peptide‐1 protects against chronic intermittent hypoxia by improving myocardial energy metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019; 481: 95–103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
