Comparative Evaluation Between the RealStar Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit and the AmpliSens Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii)-FRT PCR Kit for Detecting P. jirovecii in Non-HIV Immunocompromised Patients
- PMID: 30430780
- PMCID: PMC6240529
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.2.176
Comparative Evaluation Between the RealStar Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit and the AmpliSens Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii)-FRT PCR Kit for Detecting P. jirovecii in Non-HIV Immunocompromised Patients
Abstract
Background: Real-time PCR is more sensitive than microscopic examination for detecting Pneumocystis jirovecii. We compared the performance of two assays for detecting P. jirovecii DNA: the RealStar Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit 1.0 CE (Altona Diagnostics, Hamburg, Germany) and the AmpliSens Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii)-FRT PCR kit (InterLabService Ltd., Moscow, Russia).
Methods: We used 159 samples from the lower respiratory tract (112 bronchoalveolar lavage [BAL] fluid, 37 sputum, and 10 endotracheal aspirate [ETA] samples) of non-HIV immunocompromised patients. Nested PCR and sequencing were used to resolve discordant results. The performance of the two assays was evaluated according to clinical categories (clinical Pneumocystis pneumonia [PCP], possible PCP, or unlikely PCP) based on clinical and radiological observations.
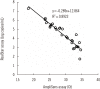
Results: The positive and negative percent agreement values were 100% (95% confidence interval [CI], 85.4-100%) and 96.6% (95% CI, 90.9-98.9%), respectively, and kappa was 0.92 (95% CI, 0.84-0.99). P. jirovecii DNA load was significantly higher in the clinical PCP group than in the other groups (P<0.05). When stratified by sample type, the positive rate for BAL fluids from the clinical PCP group was 100% using either assay, whereas the positive rate for sputum/ETA samples was only 20%.
Conclusions: The two assays showed similar diagnostic performance and detected low P. jirovecii burden in BAL fluids. Both assays may be useful as routine methods for detecting P. jirovecii DNA in a clinical laboratory setting, though their results should be interpreted considering sample type.
Keywords: AmpliSens Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii)-FRT PCR; Performance; Pneumocystis jirovecii; Pneumocystis pneumonia; Real-time PCR; RealStar Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR.
© The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas CF, Jr, Limper AH. Pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2487–2498. - PubMed
-
- White PL, Backx M, Barnes RA. Diagnosis and management of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017;15:435–447. - PubMed
-
- Alanio A, Hauser PM, Lagrou K, Melchers WJ, Helweg-Larsen J, Matos O, et al. ECIL guidelines for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with haematological malignancies and stem cell transplant recipients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71:2386–2396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

