Ranking of osteogenic potential of physical exercises in postmenopausal women based on femoral neck strains
- PMID: 29617448
- PMCID: PMC5884624
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195463
Ranking of osteogenic potential of physical exercises in postmenopausal women based on femoral neck strains
Abstract
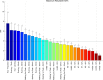
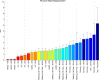
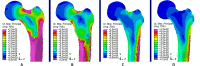
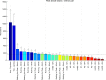
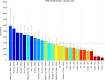
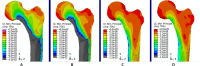
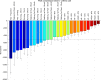
The current study aimed to assess the potential of different exercises triggering an osteogenic response at the femoral neck in a group of postmenopausal women. The osteogenic potential was determined by ranking the peak hip contact forces (HCFs) and consequent peak tensile and compressive strains at the superior and inferior part of the femoral neck during activities such as (fast) walking, running and resistance training exercises. Results indicate that fast walking (5-6 km/h) running and hopping induced significantly higher strains at the femoral neck than walking at 4 km/h which is considered a baseline exercise for bone preservation. Exercises with a high fracture risk such as hopping, need to be considered carefully especially in a frail elderly population and may therefore not be suitable as a training exercise. Since superior femoral neck frailness is related to elevated hip fracture risk, exercises such as fast walking (above 5 km/h) and running can be highly recommended to stimulate this particular area. Our results suggest that a training program including fast walking (above 5 km/h) and running exercises may increase or preserve the bone mineral density (BMD) at the femoral neck.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Boonen S, Dejaeger E, Vanderschueren D, Venken K, Bogaerts A, Verschueren S, et al. Osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture occurrence and prevention in the elderly: a geriatric perspective. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. Elsevier Ltd; 2008;22(5):765–85. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2008.07.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frost HM. From Wolff’s law to the Utah paradigm: Insights about bone physiology and its clinical applications Vol. 262, Anatomical Record; 2001. p. 398–419. - PubMed
-
- Frost HM. Bone’s mechanostat: A 2003 update. Anat Rec. Wiley Online Library; 2003;275A(2):1081–101. - PubMed
-
- Bassett CAL, Becker RO. Generation of electric potentials by bone in response to mechanical stress. Science (80-). American Association for the Advancement of Science; 1962;137(3535):1063–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

