TALE-induced bHLH transcription factors that activate a pectate lyase contribute to water soaking in bacterial spot of tomato
- PMID: 28100489
- PMCID: PMC5293091
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1620407114
TALE-induced bHLH transcription factors that activate a pectate lyase contribute to water soaking in bacterial spot of tomato
Abstract
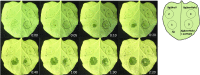
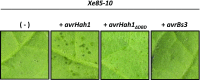
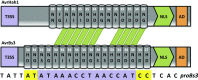
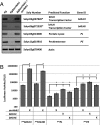
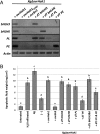
AvrHah1 [avirulence (avr) gene homologous to avrBs3 and hax2, no. 1] is a transcription activator-like (TAL) effector (TALE) in Xanthomonas gardneri that induces water-soaked disease lesions on fruits and leaves during bacterial spot of tomato. We observe that water from outside the leaf is drawn into the apoplast in X. gardneri-infected, but not X. gardneriΔavrHah1 (XgΔavrHah1)-infected, plants, conferring a dark, water-soaked appearance. The pull of water can facilitate entry of additional bacterial cells into the apoplast. Comparing the transcriptomes of tomato infected with X. gardneri vs. XgΔavrHah1 revealed the differential up-regulation of two basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors with predicted effector binding elements (EBEs) for AvrHah1. We mined our RNA-sequencing data for differentially up-regulated genes that could be direct targets of the bHLH transcription factors and therefore indirect targets of AvrHah1. We show that two pectin modification genes, a pectate lyase and pectinesterase, are targets of both bHLH transcription factors. Designer TALEs (dTALEs) for the bHLH transcription factors and the pectate lyase, but not for the pectinesterase, complement water soaking when delivered by XgΔavrHah1 By perturbing transcriptional networks and/or modifying the plant cell wall, AvrHah1 may promote water uptake to enhance tissue damage and eventual bacterial egression from the apoplast to the leaf surface. Understanding how disease symptoms develop may be a useful tool for improving the tolerance of crops from damaging disease lesions.
Keywords: TAL effector; Xanthomonas bacterial spot; water soaking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ma X, Lewis Ivey ML, Miller SA. First report of Xanthomonas gardneri causing bacterial spot of tomato in Ohio and Michigan. Plant Dis. 2011;95(12):1584. - PubMed
-
- Quezado-Duval AM, Leite RP, Jr, Truffi D, Camargo LEA. Outbreaks of bacterial spot caused by Xanthomonas gardneri on processing tomato in central-west Brazil. Plant Dis. 2004;88(2):157–161. - PubMed
-
- Schornack S, Minsavage GV, Stall RE, Jones JB, Lahaye T. Characterization of AvrHah1, a novel AvrBs3-like effector from Xanthomonas gardneri with virulence and avirulence activity. New Phytol. 2008;179(2):546–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

