A Monoclonal Antibody to Cryptococcus neoformans Glucuronoxylomannan Manifests Hydrolytic Activity for Both Peptides and Polysaccharides
- PMID: 27872188
- PMCID: PMC5241721
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.767582
A Monoclonal Antibody to Cryptococcus neoformans Glucuronoxylomannan Manifests Hydrolytic Activity for Both Peptides and Polysaccharides
Abstract
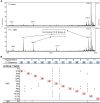
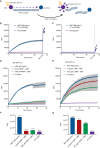
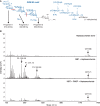
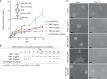
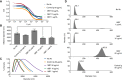
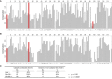
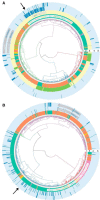
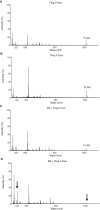
Studies in the 1980s first showed that some natural antibodies were "catalytic" and able to hydrolyze peptide or phosphodiester bonds in antigens. Many naturally occurring catalytic antibodies have since been isolated from human sera and associated with positive and negative outcomes in autoimmune disease and infection. The function and prevalence of these antibodies, however, remain unclear. A previous study suggested that the 18B7 monoclonal antibody against glucuronoxylomannan (GXM), the major component of the Cryptococcus neoformans polysaccharide capsule, hydrolyzed a peptide antigen mimetic. Using mass spectrometry and Förster resonance energy transfer techniques, we confirm and characterize the hydrolytic activity of 18B7 against peptide mimetics and show that 18B7 is able to hydrolyze an oligosaccharide substrate, providing the first example of a naturally occurring catalytic antibody for polysaccharides. Additionally, we show that the catalytic 18B7 antibody increases release of capsular polysaccharide from fungal cells. A serine protease inhibitor blocked peptide and oligosaccharide hydrolysis by 18B7, and a putative serine protease-like active site was identified in the light chain variable region of the antibody. An algorithm was developed to detect similar sites present in unique antibody structures in the Protein Data Bank. The putative site was found in 14 of 63 (22.2%) catalytic antibody structures and 119 of 1602 (7.4%) antibodies with no annotation of catalytic activity. The ability of many antibodies to cleave antigen, albeit slowly, supports the notion that this activity is an important immunoglobulin function in host defense. The discovery of GXM hydrolytic activity suggests new therapeutic possibilities for polysaccharide-binding antibodies.
Keywords: Cryptococcus neoformans; antibody; catalytic antibody; computational biology; enzyme kinetics; monoclonal antibody; protein motif; serine protease; structural motif.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Raso V., and Stollar B. D. (1975) The antibody-enzyme analogy. Comparison of enzymes and antibodies specific for phosphopyridoxyltyrosine. Biochemistry 14, 591–599 - PubMed
-
- Jencks W. P. (1969) Catalysis in Chemistry and Enzymology, p. 288, McGraw-Hill, New York
-
- Paul S., Volle D. J., Beach C. M., Johnson D. R., Powell M. J., and Massey R. J. (1989) Catalytic hydrolysis of vasoactive intestinal peptide by human autoantibody. Science 244, 1158–1162 - PubMed
-
- Shuster A. M., Gololobov G. V., Kvashuk O. A., Bogomolova A. E., Smirnov I. V., and Gabibov A. G. (1992) DNA hydrolyzing autoantibodies. Science 256, 665–667 - PubMed
-
- Li L., Paul S., Tyutyulkova S., Kazatchkine M. D., and Kaveri S. (1995) Catalytic activity of anti-thyroglobulin antibodies. J. Immunol. 154, 3328–3332 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

