Human autoreactive T cells recognize CD1b and phospholipids
- PMID: 26621732
- PMCID: PMC4720340
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1520947112
Human autoreactive T cells recognize CD1b and phospholipids
Abstract
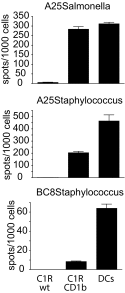
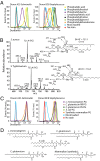
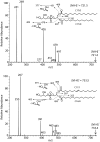
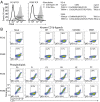
In contrast with the common detection of T cells that recognize MHC, CD1a, CD1c, or CD1d proteins, CD1b autoreactive T cells have been difficult to isolate in humans. Here we report the development of polyvalent complexes of CD1b proteins and carbohydrate backbones (dextramers) and their use in identifying CD1b autoreactive T cells from human donors. Activation is mediated by αβ T-cell receptors (TCRs) binding to CD1b-phospholipid complexes, which is sufficient to activate autoreactive responses to CD1b-expressing cells. Using mass spectrometry and T-cell responses to scan through the major classes of phospholipids, we identified phosphatidylglycerol (PG) as the immunodominant lipid antigen. T cells did not discriminate the chemical differences that distinguish mammalian PG from bacterial PG. Whereas most models of T-cell recognition emphasize TCR discrimination of differing self and foreign structures, CD1b autoreactive T cells recognize lipids with dual self and foreign origin. PG is rare in the cellular membranes that carry CD1b proteins. However, bacteria and mitochondria are rich in PG, so these data point to a more general mechanism of immune detection of infection- or stress-associated lipids.
Keywords: CD1b; T cell; dendritic cell; lipid antigen; self-antigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
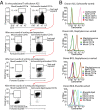
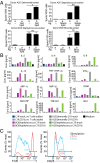
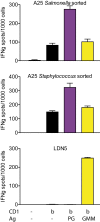
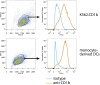
Comment in
-
Phospholipid signals of microbial infection for the human immune system.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jan 12;113(2):251-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522318113. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26719422 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dougan SK, Kaser A, Blumberg RS. CD1 expression on antigen-presenting cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;314:113–141. - PubMed
-
- Jackman RM, et al. The tyrosine-containing cytoplasmic tail of CD1b is essential for its efficient presentation of bacterial lipid antigens. Immunity. 1998;8(3):341–351. - PubMed
-
- Porcelli S, Morita CT, Brenner MB. CD1b restricts the response of human CD4-8- T lymphocytes to a microbial antigen. Nature. 1992;360(6404):593–597. - PubMed
-
- Moody DB, et al. Structural requirements for glycolipid antigen recognition by CD1b-restricted T cells. Science. 1997;278(5336):283–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

