Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is present in pancreatic acinar cells and regulates amylase secretion through cAMP
- PMID: 26542397
- PMCID: PMC4698438
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00293.2015
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is present in pancreatic acinar cells and regulates amylase secretion through cAMP
Abstract
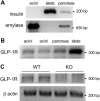
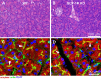
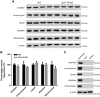
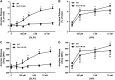
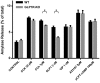
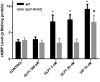
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a glucoincretin hormone that can act through its receptor (GLP-1R) on pancreatic β-cells and increase insulin secretion and production. GLP-1R agonists are used clinically to treat type 2 diabetes. GLP-1 may also regulate the exocrine pancreas at multiple levels, including inhibition through the central nervous system, stimulation indirectly through insulin, and stimulation directly on acinar cells. However, it has been unclear whether GLP-1R is present in pancreatic acini and what physiological functions these receptors regulate. In the current study we utilized GLP-1R knockout (KO) mice to study the role of GLP-1R in acinar cells. RNA expression of GLP-1R was detected in acutely isolated pancreatic acini. Acinar cell morphology and expression of digestive enzymes were not affected by loss of GLP-1R. GLP-1 induced amylase secretion in wild-type (WT) acini. In GLP-1R KO mice, this effect was abolished, whereas vasoactive intestinal peptide-induced amylase release in KO acini showed a pattern similar to that in WT acini. GLP-1 stimulated cAMP production and increased protein kinase A-mediated protein phosphorylation in WT acini, and these effects were absent in KO acini. These data show that GLP-1R is present in pancreatic acinar cells and that GLP-1 can regulate secretion through its receptor and cAMP signaling pathway.
Keywords: amylase secretion; cAMP; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; pancreatic acini.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad SR, Swann J. Exenatide and rare adverse events. N Engl J Med 358: 1970–1972, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Baldescu R, Chirulescu Z. Study of interrelationship between Zn, Ca and Mg seric concentrations in healthy subjects comparatively with diverse forms of cancer. Rom J Intern Med 32: 203–208, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Ban K, Noyan-Ashraf MH, Hoefer J, Bolz SS, Drucker DJ, Husain M. Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Circulation 117: 2340–2350, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Buteau J, Foisy S, Joly E, Prentki M. Glucagon-like peptide 1 induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation via transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Diabetes 52: 124–132, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Buteau J, Foisy S, Rhodes CJ, Carpenter L, Biden TJ, Prentki M. Protein kinase Cξ activation mediates glucagon-like peptide-1-induced pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. Diabetes 50: 2237–2243, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

