Chronic exposure to exogenous glucocorticoids primes microglia to pro-inflammatory stimuli and induces NLRP3 mRNA in the hippocampus
- PMID: 24485491
- PMCID: PMC3912460
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.11.006
Chronic exposure to exogenous glucocorticoids primes microglia to pro-inflammatory stimuli and induces NLRP3 mRNA in the hippocampus
Abstract
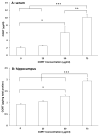
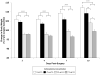
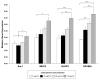
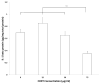
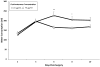
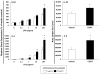
Chronic stress as well as chronic treatment with glucocorticoids (GCs) primes the neuroinflammatory response to a subsequent pro-inflammatory challenge. However, it remains unclear whether chronic GCs sensitize the response of key CNS immune substrates (i.e. microglia) to pro-inflammatory stimuli. In the present set of studies, male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent sham surgery or were adrenalectomized and then treated with varying concentrations of corticosterone (CORT; 0, 25, 50, and 75 μg/ml) administered in their drinking water. After 10 days of CORT exposure, whole hippocampus was collected and expression of glial activation markers measured or hippocampal microglia were isolated and challenged with LPS to probe for CORT-induced sensitization of pro-inflammatory responses. Chronic CORT exposure increased the gene expression of NLRP3, Iba-1, MHCII, and NF-κBIα in a concentration dependent manner. Chronic CORT (75 μg/ml) exposure potentiated the microglial proinflammatory response (TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6 and NLRP3) to LPS compared to the microglial response of sham surgery animals treated with vehicle. The present set of results demonstrate that chronic exposure to GCs primes microglia to pro-inflammatory stimuli and add to a growing body of evidence suggesting that a permissive function of GCs is that of an endogenous danger signal or alarmin.
Keywords: Glucocorticoids; Inflammasome; Microglia; Neuroinflammation; Priming; Stress.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Audet MC, Jacobson-Pick S, Wann BP, Anisman H. Social defeat promotes specific cytokine variations within the prefrontal cortex upon subsequent aggressive or endotoxin challenges. Brain, behavior, and immunity. 2011;25:1197–1205. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Krady JK, Levison SW. Interleukin-1: a master regulator of neuroinflammation. Journal of neuroscience research. 2004;78:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi ME. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81:1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

