Lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin (IL)-4 receptor-α expression and corresponding sensitivity to the M2 promoting effects of IL-4 are impaired in microglia of aged mice
- PMID: 22024136
- PMCID: PMC3288757
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.10.003
Lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin (IL)-4 receptor-α expression and corresponding sensitivity to the M2 promoting effects of IL-4 are impaired in microglia of aged mice
Abstract
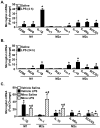
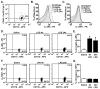
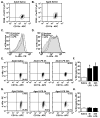
In several models of aging, microglia become more inflammatory and reactive to immune challenges. For example, peripheral LPS injection causes exaggerated microglial activation associated with prolonged sickness and depressive-like behavior in aged BALB/c mice. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine the extent to which age-related amplified microglial activation was associated with reduced sensitivity to the anti-inflammatory and M2 promoting cytokines interleukin (IL)-10 and IL-4. In initial studies with adult mice, LPS induced a time-dependent increase in M1 and M2 mRNA profiles in microglia. Furthermore, peripheral LPS injection markedly increased surface expression of IL-4 receptor-alpha (IL-4Rα), but not IL-10 receptor-1 (IL-10R1) on microglia. In BV-2 cells, IL-4, but not IL-10, re-directed LPS-activated microglia towards an M2 phenotype. Based on these findings, comparisons of M1 and M2 activation profiles, induction of IL-4Rα, and sensitivity to IL-4 were determined in microglia from adult (3-4 mo) and aged (18-22 mo) mice. In aged microglia, LPS promoted an exaggerated and prolonged M1 and M2 profile compared to adults. Moreover, IL-4Rα protein was not increased on aged microglia following LPS injection. To determine the consequence of impaired IL-4Rα upregulation, adult and aged mice were injected with LPS and activated microglia were then isolated and treated ex vivo with IL-4. While ex vivo IL-4 induced an M2 profile in activated microglia from adult mice, activated microglia from aged mice retained a prominent M1 profile. These data indicate that activated microglia from aged mice are less sensitive to the anti-inflammatory and M2-promoting effects of IL-4.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

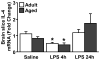
References
-
- Alexopoulos GS. Depression in the elderly. Lancet. 2005;365:1961. - PubMed
-
- Allen JB, Wong HL, Costa GL, Bienkowski MJ, Wahl SM. Suppression of monocyte function and differential regulation of IL-1 and IL-1ra by IL-4 contribute to resolution of experimental arthritis. J Immunol. 1993;151:4344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

