Defects in very long chain fatty acid synthesis enhance alpha-synuclein toxicity in a yeast model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 21264320
- PMCID: PMC3019226
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015946
Defects in very long chain fatty acid synthesis enhance alpha-synuclein toxicity in a yeast model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
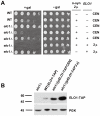
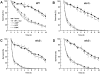
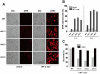
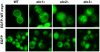
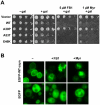
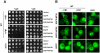
We identified three S. cerevisiae lipid elongase null mutants (elo1Δ, elo2Δ, and elo3Δ) that enhance the toxicity of alpha-synuclein (α-syn). These elongases function in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to catalyze the elongation of medium chain fatty acids to very long chain fatty acids, which is a component of sphingolipids. Without α-syn expression, the various elo mutants showed no growth defects, no reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, and a modest decrease in survival of aged cells compared to wild-type cells. With (WT, A53T or E46K) α-syn expression, the various elo mutants exhibited severe growth defects (although A30P had a negligible effect on growth), ROS accumulation, aberrant protein trafficking, and a dramatic decrease in survival of aged cells compared to wild-type cells. Inhibitors of ceramide synthesis, myriocin and FB1, were extremely toxic to wild-type yeast cells expressing (WT, A53T, or E46K) α-syn but much less toxic to cells expressing A30P. The elongase mutants and ceramide synthesis inhibitors enhance the toxicity of WT α-syn, A53T and E46K, which transit through the ER, but have a negligible effect on A30P, which does not transit through the ER. Disruption of ceramide-sphingolipid homeostasis in the ER dramatically enhances the toxicity of α-syn (WT, A53T, and E46K).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Moore DJ, West AB, Dawson VL, Dawson TM. Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:57–87. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Sleiman PM, Healy DG, Wood NW. Causes of Parkinson's disease: genetics of DJ-1. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Recchia A, Debetto P, Negro A, Guidolin D, Skaper SD, et al. Alpha-synuclein and Parkinson's disease. Faseb J. 2004;18:617–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

