Classification of alcohol abuse by plasma protein biomarkers
- PMID: 20299005
- PMCID: PMC2890298
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.01.028
Classification of alcohol abuse by plasma protein biomarkers
Abstract
Background: Biochemical diagnostics of ethanol intake would improve alcohol abuse treatment and have applications in clinical trial and public safety settings. Self-reporting of alcohol use has clinical utility but lacks the desired reliability. Previously, proposed single-analyte biochemical tests of alcohol intake suffer from low sensitivity and specificity or examine only acute drinking and have therefore seen limited clinical use.
Methods: To address this unmet need, plasma protein biomarker discovery and validation were performed with an alcohol self-administering nonhuman primate model system to develop a diagnostic that accurately classifies subjects into nondrinking, nonabusive drinking, and abusive drinking categories.
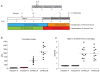
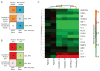
Results: A 17-plasma protein panel was determined that correctly classifies abusive drinking with 100% sensitivity and also differentiates any level of drinking from alcohol abstinence with 88% accuracy.
Conclusions: The biomarker panel reflects changes in multiple organ systems and suggests robust changes in the plasma proteome with drinking that might serve as a sensitive and specific diagnostic test. The specific plasma proteins altered with alcohol self-administration might represent indicators of alcohol-induced stress on a variety of organ systems.
Copyright 2010 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Harwood H. Updating Estimates of the Economic Costs of Alcohol Abuse in the United States: Estimates, Update Methods, and Data. Rockville, MD: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism; 2000.
-
- Hannuksela ML, Liisanantti MK, Nissinen AE, Savolainen MJ. Biochemical markers of alcoholism. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007;45:953–961. - PubMed
-
- Phillips M. Sweat-patch testing detects inaccurate self-reports of alcohol consumption. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1984;8:51–53. - PubMed
-
- Toneatto T, Sobell LC, Sobell MB. Predictors of alcohol abusers’ inconsistent self-reports of their drinking and life events. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992;16:542–546. - PubMed
-
- Pernanen K. Validity of survey data on alcohol use. In: Gibbons, et al., editors. Research Advances in Alcohol and Drug Problems. New York: 1974. pp. 355–374.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

