ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17513501
- PMCID: PMC1913739
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.048041
ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in Arabidopsis
Abstract
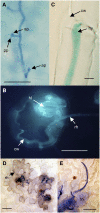
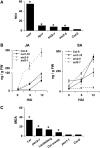
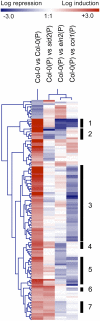
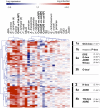
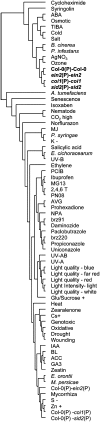
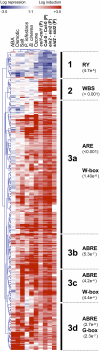
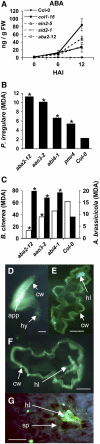
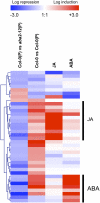
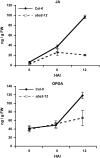
Analyses of Arabidopsis thaliana defense response to the damping-off oomycete pathogen Pythium irregulare show that resistance to P. irregulare requires a multicomponent defense strategy. Penetration represents a first layer, as indicated by the susceptibility of pen2 mutants, followed by recognition, likely mediated by ERECTA receptor-like kinases. Subsequent signaling of inducible defenses is predominantly mediated by jasmonic acid (JA), with insensitive coi1 mutants showing extreme susceptibility. In contrast with the generally accepted roles of ethylene and salicylic acid cooperating with or antagonizing, respectively, JA in the activation of defenses against necrotrophs, both are required to prevent disease progression, although much less so than JA. Meta-analysis of transcriptome profiles confirmed the predominant role of JA in activation of P. irregulare-induced defenses and uncovered abscisic acid (ABA) as an important regulator of defense gene expression. Analysis of cis-regulatory sequences also revealed an unexpected overrepresentation of ABA response elements in promoters of P. irregulare-responsive genes. Subsequent infections of ABA-related and callose-deficient mutants confirmed the importance of ABA in defense, acting partly through an undescribed mechanism. The results support a model for ABA affecting JA biosynthesis in the activation of defenses against this oomycete.
Figures

References
-
- Abuqamar, S., Chen, X., Dhawan, R., Bluhm, B., Salmeron, J., Lam, S., Dietrich, R.A., and Mengiste, T. (2006). Expression profiling and mutant analysis reveals complex regulatory networks involved in Arabidopsis response to Botrytis infection. Plant J. 48 28–44. - PubMed
-
- Aist, J. (1976). Papillae and related wound plugs of plant cells. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 14 145–163.
-
- Anderson, J.P., Badruzsaufari, E., Schenk, P.M., Manners, J.M., Desmond, O.J., Ehlert, C., Maclean, D.J., Ebert, P.R., and Kazan, K. (2004). Antagonistic interaction between abscisic acid and jasmonate-ethylene signaling pathways modulates defense gene expression and disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16 3460–3479. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Assaad, F.F., Qiu, J.L., Youngs, H., Ehrhardt, D., Zimmerli, L., Kalde, M., Wanner, G., Peck, S.C., Edwards, H., Ramonell, K., Somerville, C.R., and Thordal-Christensen, H. (2004). The PEN1 syntaxin defines a novel cellular compartment upon fungal attack and is required for the timely assembly of papillae. Mol. Biol. Cell 15 5118–5129. - PMC - PubMed
NOTE ADDED IN PROOF
-
- When this work was in press, Hernández-Blanco et al. (2007) published results concerning the role of ABA in disease resistance that support results described in this article.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

