Soluble proteins produced by probiotic bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell survival and growth
- PMID: 17258729
- PMCID: PMC3036990
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.022
Soluble proteins produced by probiotic bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell survival and growth
Abstract
Background & aims: Increased inflammatory cytokine levels and intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis leading to disruption of epithelial integrity are major pathologic factors in inflammatory bowel diseases. The probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) and factors recovered from LGG broth culture supernatant (LGG-s) prevent cytokine-induced apoptosis in human and mouse intestinal epithelial cells by regulating signaling pathways. Here, we purify and characterize 2 secreted LGG proteins that regulate intestinal epithelial cell antiapoptotic and proliferation responses.
Methods: LGG proteins were purified from LGG-s, analyzed, and used to generate polyclonal antibodies for immunodepletion of respective proteins from LGG-conditioned cell culture media (CM). Mouse colon epithelial cells and cultured colon explants were treated with purified proteins in the absence or presence of tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Akt activation, proliferation, tissue injury, apoptosis, and caspase-3 activation were determined.
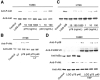
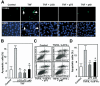
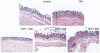
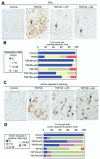
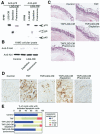
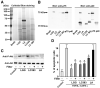
Results: We purified 2 novel proteins, p75 (75 kilodaltons) and p40 (40 kilodaltons), from LGG-s. Each of these purified protein preparations activated Akt, inhibited cytokine-induced epithelial cell apoptosis, and promoted cell growth in human and mouse colon epithelial cells and cultured mouse colon explants. TNF-induced colon epithelial damage was significantly reduced by p75 and p40. Immunodepletion of p75 and p40 from LGG-CM reversed LGG-CM activation of Akt and its inhibitory effects on cytokine-induced apoptosis and loss of intestinal epithelial cells.
Conclusions: p75 and p40 are the first probiotic bacterial proteins demonstrated to promote intestinal epithelial homeostasis through specific signaling pathways. These findings suggest that probiotic bacterial components may be useful for preventing cytokine-mediated gastrointestinal diseases.
Figures

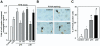
References
-
- Sartor RB. Mucosal immunology and mechanisms of gastrointestinal inflammation. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Sleisenger MH, editors. Sleisenger & Fordtran’s gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 7th ed. I. Saunders; Philadelphia: 2002. pp. 21–51.
-
- El-Assal ON, Besner GE. HB-EGF enhances restitution after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion via PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK1/2 activation. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:609–625. - PubMed
-
- Matsuura M, Okazaki K, Nishio A, Nakase H, Tamaki H, Uchida K, Nishi T, Asada M, Kawasaki K, Fukui T, Yoshizawa H, Ohashi S, Inoue S, Kawanami C, Hiai H, Tabata Y, Chiba T. Therapeutic effects of rectal administration of basic fibroblast growth factor on experimental murine colitis. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:975–986. - PubMed
-
- McCole DF, Rogler G, Varki N, Barrett KE. Epidermal growth factor partially restores colonic ion transport responses in mouse models of chronic colitis. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:591–608. - PubMed
-
- Sinha A, Nightingale J, West KP, Berlanga-Acosta J, Playford RJ. Epidermal growth factor enemas with oral mesalamine for mild-to-moderate left-sided ulcerative colitis or proctitis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:350–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

