Complex I deficiency primes Bax-dependent neuronal apoptosis through mitochondrial oxidative damage
- PMID: 16365298
- PMCID: PMC1323177
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508215102
Complex I deficiency primes Bax-dependent neuronal apoptosis through mitochondrial oxidative damage
Abstract
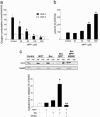
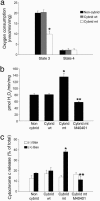
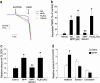
Dysfunction of mitochondrial complex I is a feature of human neurodegenerative diseases such as Leber hereditary optic neuropathy and Parkinson's disease. This mitochondrial defect is associated with a recruitment of the mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathway in vivo. However, in isolated brain mitochondria, complex I dysfunction caused by either pharmacological or genetic means fails to directly activate this cell death pathway. Instead, deficits of complex I stimulate intramitochondrial oxidative stress, which, in turn, increase the releasable soluble pool of cytochrome c within the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Upon mitochondrial permeabilization by the cell death agonist Bax, more cytochrome c is released to the cytosol from brain mitochondria with impaired complex I activity. Given these results, we propose a model in which defects of complex I lower the threshold for activation of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis by Bax, thereby rendering compromised neurons more prone to degenerate. This molecular scenario may have far-reaching implications for the development of effective neuroprotective therapies for these incurable illnesses.
Figures


References
-
- Wallace, D. C., Singh, G., Lott, M. T., Hodge, J. A., Schurr, T. G., Lezza, A. M. S., Elsas, L. J. & Nikoskelainen, E. K. (1988) Science 242, 1427-1430. - PubMed
-
- Parker, W. D., Jr., Boyson, S. J. & Parks, J. K. (1989) Ann. Neurol. 26, 719-723. - PubMed
-
- Schapira, A. H., Cooper, J. M., Dexter, D., Clark, J. B., Jenner, P. & Marsden, C. D. (1990) J. Neurochem. 54, 823-827. - PubMed
-
- Dauer, W. & Przedborski, S. (2003) Neuron 39, 889-909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

