HIF-1alpha: a master regulator of innate host defenses?
- PMID: 16007247
- PMCID: PMC1159156
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25740
HIF-1alpha: a master regulator of innate host defenses?
Abstract
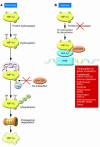
In the days following infection, when the human body develops and refines antibodies and prepares to mount an adaptive immune response, the bulwark of innate host defense against microbial infection is the polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN). PMNs seek out, identify, engulf, and sterilize invading microbes using both O2-dependent and O2-independent antimicrobial systems. A decrease in PMN numbers or function caused by immunosuppression or disease increases the risk of infection. In this issue of the JCI, Peyssonnaux et al. identify a novel and essential role for hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in regulating several important PMN functions relevant to host defense, including transcription of cationic antimicrobial polypeptides and induction of NO synthase.
Figures
Comment on
-
HIF-1alpha expression regulates the bactericidal capacity of phagocytes.J Clin Invest. 2005 Jul;115(7):1806-15. doi: 10.1172/JCI23865. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16007254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semenza GL. Hydroxylation of HIF-1: oxygen sensing at the molecular level [review] Physiology (Bethesda). 2004;19:176–182. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL. HIF-1 and human disease: one highly involved factor [review] Genes Dev. 2000;14:1983–1991. - PubMed
-
- Bruick RK. Oxygen sensing in the hypoxic response pathway: regulation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor [review] Genes Dev. 2003;17:2614–2623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

