Astrocytes regulate inhibitory synapse formation via Trk-mediated modulation of postsynaptic GABAA receptors
- PMID: 15814795
- PMCID: PMC6725365
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3980-04.2005
Astrocytes regulate inhibitory synapse formation via Trk-mediated modulation of postsynaptic GABAA receptors
Abstract
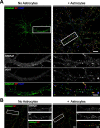
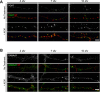
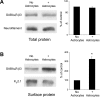
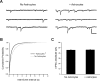
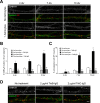
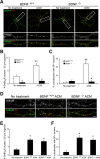
Astrocytes promote the formation and function of excitatory synapses in the CNS. However, whether and how astrocytes modulate inhibitory synaptogenesis are essentially unknown. We asked whether astrocytes regulate the formation of inhibitory synapses between hippocampal neurons during maturation in vitro. Neuronal coculture with astrocytes or treatment with astrocyte-conditioned medium (ACM) increased the number of inhibitory presynaptic terminals, the frequency of miniature IPSCs, and the number and synaptic localization of GABA(A) receptor (GABA(A)R) clusters during the first 10 d in vitro. We asked whether neurotrophins, which are potent modulators of inhibitory synaptic structure and function, mediate the effects of astrocytes on inhibitory synapses. ACM from BDNF- or tyrosine receptor kinase B (TrkB)-deficient astrocytes increased inhibitory presynaptic terminals and postsynaptic GABA(A)R clusters in wild-type neurons, suggesting that BDNF and TrkB expression in astrocytes is not required for these effects. In contrast, although the increase in the number of inhibitory presynaptic terminals persisted, no increase was observed in postsynaptic GABA(A)R clusters after ACM treatment of hippocampal neurons lacking BDNF or TrkB. These results suggest that neurons, not astrocytes, are the relevant source of BDNF and are the site of TrkB activation required for postsynaptic GABA(A)R modulation. These data also suggest that astrocytes may modulate postsynaptic development indirectly by stimulating Trk signaling between neurons. Together, these data show that astrocytes modulate inhibitory synapse formation via distinct presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms.
Figures

References
-
- Alderson RF, Curtis R, Alterman AL, Lindsay RM, DiStefano PS (2000) Truncated TrkB mediates the endocytosis and release of BDNF and neurotrophin-4/5 by rat astrocytes and Schwann cells in vitro. Brain Res 871: 210-222. - PubMed
-
- Brunig I, Penschuck S, Berninger B, Benson J, Fritschy JM (2001) BDNF reduces miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents by rapid downregulation of GABA(A) receptor surface expression. Eur J Neurosci 13: 1320-1328. - PubMed
-
- Christopherson KS, Ullian EM, Stokes CCA, Mullowney CE, Hell JW, Agah A, Lawler J, Mosher DF, Bornstein P, Barres BA (2005) Thrombospondins are astrocyte-secreted proteins that promote CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 120: 421-433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
