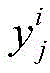CN110580943B - An intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication - Google Patents
An intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110580943B CN110580943B CN201910581225.3A CN201910581225A CN110580943B CN 110580943 B CN110580943 B CN 110580943B CN 201910581225 A CN201910581225 A CN 201910581225A CN 110580943 B CN110580943 B CN 110580943B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- neural network
- lora communication
- infusion
- pager
- output
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M5/00—Devices for bringing media into the body in a subcutaneous, intra-vascular or intramuscular way; Accessories therefor, e.g. filling or cleaning devices, arm-rests
- A61M5/14—Infusion devices, e.g. infusing by gravity; Blood infusion; Accessories therefor
- A61M5/168—Means for controlling media flow to the body or for metering media to the body, e.g. drip meters, counters ; Monitoring media flow to the body
- A61M5/16831—Monitoring, detecting, signalling or eliminating infusion flow anomalies
- A61M5/1684—Monitoring, detecting, signalling or eliminating infusion flow anomalies by detecting the amount of infusate remaining, e.g. signalling end of infusion
- A61M5/16845—Monitoring, detecting, signalling or eliminating infusion flow anomalies by detecting the amount of infusate remaining, e.g. signalling end of infusion by weight
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08C—TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR MEASURED VALUES, CONTROL OR SIMILAR SIGNALS
- G08C17/00—Arrangements for transmitting signals characterised by the use of a wireless electrical link
- G08C17/02—Arrangements for transmitting signals characterised by the use of a wireless electrical link using a radio link
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H20/00—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance
- G16H20/10—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance relating to drugs or medications, e.g. for ensuring correct administration to patients
- G16H20/17—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance relating to drugs or medications, e.g. for ensuring correct administration to patients delivered via infusion or injection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B5/00—Near-field transmission systems, e.g. inductive or capacitive transmission systems
- H04B5/70—Near-field transmission systems, e.g. inductive or capacitive transmission systems specially adapted for specific purposes
- H04B5/77—Near-field transmission systems, e.g. inductive or capacitive transmission systems specially adapted for specific purposes for interrogation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/28—Data switching networks characterised by path configuration, e.g. LAN [Local Area Networks] or WAN [Wide Area Networks]
- H04L12/44—Star or tree networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/12—Protocols specially adapted for proprietary or special-purpose networking environments, e.g. medical networks, sensor networks, networks in vehicles or remote metering networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/32—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials
- H04L9/3271—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials using challenge-response
- H04L9/3278—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials using challenge-response using physically unclonable functions [PUF]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04M—TELEPHONIC COMMUNICATION
- H04M11/00—Telephonic communication systems specially adapted for combination with other electrical systems
- H04M11/02—Telephonic communication systems specially adapted for combination with other electrical systems with bell or annunciator systems
- H04M11/022—Paging systems
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/30—Services specially adapted for particular environments, situations or purposes
- H04W4/38—Services specially adapted for particular environments, situations or purposes for collecting sensor information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W84/00—Network topologies
- H04W84/18—Self-organising networks, e.g. ad-hoc networks or sensor networks
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M2205/00—General characteristics of the apparatus
- A61M2205/18—General characteristics of the apparatus with alarm
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M2205/00—General characteristics of the apparatus
- A61M2205/35—Communication
- A61M2205/3546—Range
- A61M2205/3553—Range remote, e.g. between patient's home and doctor's office
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Arrangements For Transmission Of Measured Signals (AREA)
Abstract
本发明公开了一种基于LoRa通信的智能输液系统,包括输液监测单元、呼叫器、中继器、Lora通信模块和医护站上位机,所述输液监测单元、呼叫器通过Lora通信模块与中继器连接,所述医护站上位机通过网线与中继器连接。本发明通过LoRa无线通信技术,提高了信息传输的鲁棒性、安全性,通过设置称重校准模块,提高了数据测量的准确性。
The invention discloses an intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication, comprising an infusion monitoring unit, a pager, a repeater, a Lora communication module and a medical care station host computer. The upper computer of the medical care station is connected with the repeater through a network cable. The invention improves the robustness and security of information transmission through LoRa wireless communication technology, and improves the accuracy of data measurement by setting a weighing calibration module.
Description
技术领域technical field
本发明涉及医疗信息领域,具体涉及一种基于Lora通信的智能输液系统。The invention relates to the field of medical information, in particular to an intelligent infusion system based on Lora communication.
背景技术Background technique
智能输液系统可自动判别输液剩余剂量,预估剩余时间,判别堵针、漏针、空瓶、滴停等情况,通过物联网络把每个床位的输液状态信息实时传送到医护站上位机,使护士在医护站内便可以看到病区中每个床位的输液进程并及时更换药液,是智慧医疗的一个重要研究方向。现有的智能输液系统多采取Wifi、ZigBee 进行无线通信,传输距离较小,且容易受到干扰影响。The intelligent infusion system can automatically determine the remaining dose of the infusion, estimate the remaining time, and determine the situation of blocked needles, leaking needles, empty bottles, and dripping stops. It is an important research direction of smart medical care that nurses can see the infusion process of each bed in the ward and change the liquid in time in the medical station. The existing intelligent infusion systems mostly use Wifi and ZigBee for wireless communication, the transmission distance is small, and they are easily affected by interference.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于提供一种基于Lora通信的智能输液系统。The purpose of the present invention is to provide an intelligent infusion system based on Lora communication.
实现本发明目的的技术解决方案为:一种基于Lora通信的智能输液系统,包括输液监测单元、中继器、呼叫器、无线通信模块及医护站上位机,所述输液监测单元、呼叫器通过Lora通信模块与中继器连接,所述医护站上位机通过网线与中继器连接。输液监测单元负责监测药液的重量、输液进度等信息,并通过 LoRa无线通信技术传至中继器;呼叫器用于发出紧急呼叫信号,并通过LoRa 无线通信技术传至中继器;中继器从输液监测单元获取输液相关信息,从呼叫器获取呼叫信号,并通过网线传至医护站上位机;医护站上位机为中继器提供电源的同时,根据从中继器获得的信息发出输液结束提醒或呼叫提醒。The technical solution to achieve the purpose of the present invention is: an intelligent infusion system based on Lora communication, including an infusion monitoring unit, a repeater, a pager, a wireless communication module and a medical care station host computer, the infusion monitoring unit and the pager pass through. The Lora communication module is connected with the repeater, and the upper computer of the medical station is connected with the repeater through a network cable. The infusion monitoring unit is responsible for monitoring the weight of the liquid medicine, infusion progress and other information, and transmits it to the repeater through LoRa wireless communication technology; the pager is used to send an emergency call signal and transmits it to the repeater through LoRa wireless communication technology; the repeater Obtain the infusion-related information from the infusion monitoring unit, obtain the call signal from the pager, and transmit it to the upper computer of the medical care station through the network cable; while the upper computer of the medical care station provides power to the repeater, it sends out a reminder of the end of infusion according to the information obtained from the repeater or call reminder.
与现有技术相比,本发明的优点在于:1)本发明通过LoRa无线通信技术,提高了信息传输的鲁棒性、安全性;2)本发明通过设置称重校准模块,提高了数据测量的准确性。Compared with the prior art, the advantages of the present invention are: 1) the present invention improves the robustness and security of information transmission through LoRa wireless communication technology; 2) the present invention improves data measurement by setting a weighing calibration module accuracy.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是基于LoRa通信的智能输液系统的结构图。Figure 1 is a structural diagram of an intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication.
图2是轮询Lora网关的流程图。Figure 2 is a flowchart of polling the Lora gateway.
图3是安全接入Lora网关的原理图。Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a secure access Lora gateway.
图4是本发明实施例的场地示意图。FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of a site according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图5是小波神经网络与人工鱼群算法的具体流程图。Fig. 5 is the concrete flow chart of wavelet neural network and artificial fish swarm algorithm.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和具体实施例,进一步说明本发明方案。The solution of the present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
如图1所示,基于Lora通信的智能输液系统,包括输液监测单元、中继器、呼叫器、无线通信模块及医护站上位机,所述输液监测单元、呼叫器通过Lora 通信模块与中继器连接,所述医护站上位机通过网线与中继器连接。输液监测单元负责监测药液的重量、输液进度等信息,并通过LoRa无线通信技术传至中继器;呼叫器用于发出紧急呼叫信号,并通过LoRa无线通信技术传至中继器;中继器从输液监测单元获取输液相关信息,从呼叫器获取呼叫信号,并通过网线传至医护站上位机;医护站上位机为中继器提供电源的同时,根据从中继器获得的信息发出输液结束提醒或呼叫提醒。As shown in Figure 1, the intelligent infusion system based on Lora communication includes an infusion monitoring unit, a repeater, a pager, a wireless communication module and a medical care station host computer. The infusion monitoring unit and the pager communicate with the relay through the Lora communication module. The upper computer of the medical care station is connected with the repeater through a network cable. The infusion monitoring unit is responsible for monitoring the weight of the liquid medicine, infusion progress and other information, and transmits it to the repeater through LoRa wireless communication technology; the pager is used to send an emergency call signal and transmits it to the repeater through LoRa wireless communication technology; the repeater Obtain the infusion-related information from the infusion monitoring unit, obtain the call signal from the pager, and transmit it to the upper computer of the medical care station through the network cable; while the upper computer of the medical care station provides power to the repeater, it sends out a reminder of the end of infusion according to the information obtained from the repeater or call reminder.
一些实施例中,Lora通信模块采用星型网络结构。由于Lora网关在某一时刻只能同一个终端节点进行信息的交汇,所以在无线传输的过程中,Lora通信模块采用轮询方式让节点数据按一定的周期轮流访问Lora网关,轮询流程如图 2所示。In some embodiments, the Lora communication module adopts a star network structure. Since the Lora gateway can only exchange information with one terminal node at a certain time, in the process of wireless transmission, the Lora communication module adopts the polling method to allow the node data to access the Lora gateway in turn according to a certain period. The polling process is shown in the figure. 2 shown.
通常,输液监测单元通过称重传感器测量药液的重量,进而确定输液进度。但是称重传感器容易受温度影响产生零点漂移现象,导致称重信息不准确,造成输液结束报警的提前或滞后。为应对称重传感器受温度影响产生的零点漂移现象,本发明在输液监测单元内设置称重校准模块,采用小波神经网络与人工鱼群算法对称重传感器进行零点温度漂移的补偿。Usually, the infusion monitoring unit measures the weight of the liquid medicine through a load cell to determine the infusion progress. However, the load cell is easily affected by temperature and produces a zero-point drift phenomenon, which leads to inaccurate weighing information, resulting in the advance or lag of the end of the infusion alarm. In order to deal with the zero drift phenomenon of the load cell affected by temperature, the present invention sets a weighing calibration module in the infusion monitoring unit, and uses wavelet neural network and artificial fish swarm algorithm to compensate the zero point temperature drift of the load cell.
在进行温度补偿前,首先通过固定药液重量、改变温度以及固定温度、改变药液重量两种方式,采集不同条件下称重传感器输出的电压数据;然后利用小波神经网络对数据样本进行学习,通过对自身的训练使神经网络输出与期望的输出值逐步逼近;因为小波神经网络容易陷入局部最优,所以引入人工鱼群算法对其进行检验,以便得出全局最优解。Before temperature compensation, the voltage data output by the weighing sensor under different conditions is collected by fixing the weight of the liquid medicine, changing the temperature, and fixing the temperature and changing the weight of the liquid medicine; then use the wavelet neural network to learn the data samples, Through its own training, the output of the neural network is gradually approached to the expected output value; because the wavelet neural network is easy to fall into the local optimum, the artificial fish swarm algorithm is introduced to test it in order to obtain the global optimal solution.
小波神经网络与人工鱼群算法的具体过程描述如下:The specific process of wavelet neural network and artificial fish swarm algorithm is described as follows:
(1)初始化参数:对输入层节点个数m、隐含层节点个数n、输出层节点个数l、小波的伸缩因子aj、平移因子bj、输入层与隐含层之间的连接权值vji、隐含层到输出层的连接权值wkj赋予初始值,选取隐含层神经元函数及误差函数E;(1) Initialization parameters: for the number of nodes in the input layer m, the number of nodes in the hidden layer n, the number of nodes in the output layer l, the scaling factor a j of the wavelet, the translation factor b j , the difference between the input layer and the hidden layer The connection weight v ji and the connection weight w kj from the hidden layer to the output layer are given to the initial value, and the neuron function of the hidden layer is selected. and the error function E;
(2)开始小波神经网络搜索:输入学习样本(称重传感器在不同温度条件下称量的重力)及相应的期望输出(称重传感器输出的电压),利用公式(1) 计算输出层的输出,利用公式(2)计算误差;(2) Start the wavelet neural network search: input the learning sample (gravity weighed by the load cell under different temperature conditions) and the corresponding expected output (the voltage output by the load cell), and use formula (1) to calculate the output of the output layer , using formula (2) to calculate the error;
其中,M为输入样本的模式个数,和分别为第i(i=1,2,…,M)个模式的第j(j=1,2,…,N)个期望输出和实际输出;Among them, M is the number of patterns of input samples, and are the jth (j=1, 2,...,N) expected output and actual output of the ith (i=1, 2,...,M) mode respectively;
(3)判断是否结束神经网络算法:当误差小于预先设定的某个阈值,停止神经网络的学习,转入人工鱼群算法,否则输入下一样本,回到步骤2,继续神经网络学习;(3) Judging whether to end the neural network algorithm: when the error is less than a predetermined threshold, stop the learning of the neural network, and transfer to the artificial fish swarm algorithm, otherwise input the next sample, go back to step 2, and continue the neural network learning;
(4)鱼群初始化:利用小波神经网络输出层的输出结果,对N条人工鱼进行初始化,小波神经网络的输出结果为第i条人工鱼的状态,步骤2中的误差函数为人工鱼的适应值函数,此时人工鱼群聚集在同一处,公告板上的最优解是小波神经网络的输出结果;(4) Fish school initialization: use the output result of the output layer of the wavelet neural network to initialize N artificial fish, the output result of the wavelet neural network is the state of the ith artificial fish, and the error function in step 2 is the artificial fish The fitness value function, at this time, the artificial fish groups gather in the same place, and the optimal solution on the bulletin board is the output result of the wavelet neural network;
(5)进行最优解的验证:鱼群执行觅食行为,按照一定的步长(Step),搜寻视野范围内(Visual)食物浓度更高的地方(即适应值更小、误差更小的地方),如果搜寻不到则随机前进一步,此时人工鱼的适应值改变但公告板上的最优解并不更新,当迭代一定次数,公告板的最优解始终未变,则可以判定小波神经网络的输出结果为全局最佳结果;如果鱼群在觅食过程中找到食物浓度更高的地方,则公告板上的最优解改变,并将该结果反馈给小波神经网络使其继续进行训练,如此循环直至找到全局最优解。(5) Verification of the optimal solution: the fish group performs foraging behavior, and searches for places with higher food concentration within the visual field (Visual) according to a certain step size (that is, the fitness value is smaller and the error is smaller). place), if it cannot be searched, it will move forward randomly. At this time, the fitness value of the artificial fish changes, but the optimal solution on the bulletin board is not updated. The output result of the wavelet neural network is the global best result; if the fish finds a place with higher food concentration during the foraging process, the optimal solution on the bulletin board changes, and the result is fed back to the wavelet neural network to continue. Perform training, and so on until the global optimal solution is found.
一些实施例中,所述Lora通信模块设置安全验证接入模块,利用芯片的物理不可克隆函数性质,实现Lora通信模块与输液监测单元及呼叫器的安全验证接入,安全验证接入的流程如图3所示,具体内容如下:In some embodiments, the Lora communication module is provided with a security verification access module, and the physical unclonable function property of the chip is used to realize the security verification access of the Lora communication module, the infusion monitoring unit and the pager. The process of the security verification access is as follows. As shown in Figure 3, the details are as follows:
由于每一个输液监测模块、呼叫器内的芯片制造工艺存在差异,Lora网关向不同的输液监测单元和呼叫器分别发送激励信号,会获得不同的响应信号,这些响应是独特且不可复制的,可作为每个输液监测单元或呼叫器的ID,即身份“验证码”;Lora网关将这些身份“验证码”放入存储模块,用于输液监测器及呼叫器轮询时,进行ID接入验证。Due to the differences in the chip manufacturing process in each infusion monitoring module and pager, the Lora gateway sends excitation signals to different infusion monitoring units and pagers respectively, and will obtain different response signals. These responses are unique and unreproducible, and can be As the ID of each infusion monitoring unit or pager, that is, the identity "verification code"; the Lora gateway puts these identity "verification codes" into the storage module for ID access verification when the infusion monitor and pager are polled .
如图4所示,一些实施例中,输液监测单元及呼叫器设置在病床附近,中继器和Lora通信模块设置在医院走廊。由于病床与输液监测单元及呼叫器距离较近,采用无线射频识别技术将每一张病床分别与一个输液监测单元及一个呼叫器绑定。在输液区的病床上分别设置RFID标签,对每一个输液监测器、呼叫器与病床上的标签绑定,绑定之后,医护站主机就可以区分来自不同床位的输液监测单元、呼叫器发送的信息。As shown in FIG. 4 , in some embodiments, the infusion monitoring unit and the pager are arranged near the hospital bed, and the repeater and the Lora communication module are arranged in the hospital corridor. Since the hospital bed is relatively close to the infusion monitoring unit and the pager, radio frequency identification technology is used to bind each hospital bed to an infusion monitoring unit and a pager respectively. RFID tags are set on the beds in the infusion area, and each infusion monitor and pager is bound to the label on the bed. After binding, the host of the medical station can distinguish the data sent by the infusion monitoring unit and pager from different beds. information.
为了验证本发明方案的有效性,进行如下仿真实验。In order to verify the effectiveness of the scheme of the present invention, the following simulation experiments are carried out.
一、Lora通信测试1. Lora communication test
本实施例中,Lora通信模块采用成都亿百特公司的产品E32-433T20DC,它是一款基于SEMTECH公司SX1278射频芯片的无线串口模块(UART),该模块采用TTL电平。保持E32-433T20DC产品的默认设置不变,即空中传输速率为2.4kbps、发射功率为20dBm,在存在墙壁、电子设备、光学设备等阻挡,包含4G、WiFi、微波、毫米波等干扰的环境中,进行平面穿墙测试、跨楼层测试。In this embodiment, the Lora communication module adopts the product E32-433T20DC of Chengdu Ebyte Company, which is a wireless serial port module (UART) based on the SX1278 radio frequency chip of SEMTECH Company, and the module adopts TTL level. Keep the default settings of the E32-433T20DC product unchanged, that is, the air transmission rate is 2.4kbps, and the transmit power is 20dBm. In the environment where there are obstacles such as walls, electronic equipment, optical equipment, etc., including 4G, WiFi, microwave, millimeter wave and other interference , conduct plane through-wall test and cross-floor test.
(1)平面穿墙测试(1) Plane through-wall test
首先在同一层楼的不同房间进行数据包的收发测试,在发送包为150000个的情况下,测试结果如表1。可以看出,传输路径长达60米(间隔六面墙壁) 时,丢包率仅1.187%,比Wifi、ZigBee等方式的通信质量更高。First, the data packets are sent and received in different rooms on the same floor. In the case of sending 150,000 packets, the test results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen that when the transmission path is as long as 60 meters (six walls are separated), the packet loss rate is only 1.187%, which is higher than the communication quality of Wifi, ZigBee and other methods.
表1平面穿墙测试结果表Table 1 Plane through-wall test results table
(2)跨楼层测试(2) Cross-floor test
以三楼为基准,分别向其他楼层发送数据包,测试结果如表2。可以看出,当信号传输至六楼时,丢包率仅为1.271%,比Wifi、ZigBee等方式的通信质量更高。Taking the third floor as the benchmark, data packets are sent to other floors respectively. The test results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that when the signal is transmitted to the sixth floor, the packet loss rate is only 1.271%, which is higher than the communication quality of Wifi, ZigBee and other methods.
表2跨楼层测试结果表Table 2 Cross-floor test result table
二、称重校准测试2. Weighing calibration test
在称重校准模块中,可选用的称重传感器较多,不同的称重传感器由于制造工艺存在差异而具有不同的零点温度漂移规律,因此温度补偿要依据称重传感器的自身规律而进行。这里以PT14型压力传感器为例,测量了它在不同情况下的输出电压数据,如表3。In the weighing calibration module, there are many optional weighing sensors. Different weighing sensors have different zero temperature drift laws due to differences in the manufacturing process. Therefore, the temperature compensation should be carried out according to the own laws of the weighing sensor. Taking the PT14 pressure sensor as an example, the output voltage data under different conditions are measured, as shown in Table 3.
表3 PT14型压力传感器的测量数据表Table 3 Measurement data table of PT14 pressure sensor
在表3中,t为压力传感器所处的环境温度,P是压力传感器承载的压力, UP是压力传感器的输出电压。In Table 3, t is the ambient temperature where the pressure sensor is located, P is the pressure carried by the pressure sensor, and U P is the output voltage of the pressure sensor.
完成数据采集之后,按照图5执行小波神经网络与人工鱼群算法。参数初始化包括:根据压力P的9个取值(100-108)设置小波神经网络的输入层节点为9个,根据温度t的7个取值确定输入样本的模式数为7,设置输出节点为1个用于输出结果;按照已有研究的经验,设置隐含层的节点数为16、网络的最大训练次数为500、学习速率为0.01、动量因子为0.95、训练目标误差平方和为 0.0001;隐含层神经元函数选用Morlet小波函数,其函数表达式为:After the data collection is completed, the wavelet neural network and artificial fish swarm algorithm are executed according to Figure 5. Parameter initialization includes: setting the input layer nodes of the wavelet neural network to 9 according to the 9 values of the pressure P (100-108), determining the number of modes of the input sample to 7 according to the 7 values of the temperature t, and setting the output node to 1 is used to output the results; according to the experience of existing research, set the number of nodes in the hidden layer to 16, the maximum training times of the network to 500, the learning rate to 0.01, the momentum factor to 0.95, and the training target error sum of squares to 0.0001; The hidden layer neuron function uses the Morlet wavelet function, and its function expression is:
此外,设置鱼群的规模N=20,视野Visual=0.7,步长Step=0.5,最大迭代次数为400。以上参数并不用于限定本发明,在实施例中可根据具体情况作出改进和优化。In addition, set the size of the fish school N=20, the field of view Visual=0.7, the step size Step=0.5, and the maximum number of iterations is 400. The above parameters are not intended to limit the present invention, and improvements and optimizations can be made in the embodiments according to specific conditions.
接下来进行小波神经网络的训练,将称重传感器在不同温度条件下称量的重力及输出的电压作为学习样本,利用公式(1)计算输出结果,利用公式(2)计算误差;直到计算所得的误差小于设置的阈值,转入人工鱼群算法,以小波神经网络的输出结果作为鱼群的初始状态。Next, the training of the wavelet neural network is carried out, the gravity and the output voltage of the load cell under different temperature conditions are used as the learning samples, the output result is calculated by formula (1), and the error is calculated by formula (2); If the error is less than the set threshold, it is transferred to the artificial fish swarm algorithm, and the output result of the wavelet neural network is used as the initial state of the fish swarm.
通过让人工鱼群执行觅食行为验证该输出是否为全局最优。设第i条人工鱼的当前状态为Xi,对应的适应值为Yi(由公式(2)计算所得),在其Visual范围内随机选择一个状态Xv,如公式(4),若对应的适应值Yv<Yi,则公告板上的最优解更新为Xv,并向小波神经网络进行反馈,使其继续训练以改善结果;否则,人工鱼随机前进一步,变为状态Xinext,如公式(5),而公告板无需更新。Whether the output is globally optimal is verified by letting the artificial fish perform foraging behavior. Let the current state of the i-th artificial fish be X i , and the corresponding fitness value is Y i (calculated by formula (2)), and randomly select a state X v within its Visual range, such as formula (4), if the corresponding If the fitness value Y v <Y i , the optimal solution on the bulletin board is updated to X v , and feedback is given to the wavelet neural network to continue training to improve the result; otherwise, the artificial fish randomly advances one step and becomes state X inext , as in Equation (5), and the bulletin board does not need to be updated.
Xv=Xi+Rand()*Visual (4)X v =X i +Rand()*Visual (4)
Xinext=Xi+Rand()*Step (5)X inext =X i +Rand()*Step (5)
重复以上步骤,直到小波神经网络输出最佳结果,即温度补偿达到规定误差下的最佳效果。Repeat the above steps until the wavelet neural network outputs the best result, that is, the temperature compensation reaches the best effect under the specified error.
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910581225.3A CN110580943B (en) | 2019-06-29 | 2019-06-29 | An intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910581225.3A CN110580943B (en) | 2019-06-29 | 2019-06-29 | An intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110580943A CN110580943A (en) | 2019-12-17 |
| CN110580943B true CN110580943B (en) | 2022-08-12 |
Family
ID=68810822
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910581225.3A Expired - Fee Related CN110580943B (en) | 2019-06-29 | 2019-06-29 | An intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110580943B (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112107763A (en) * | 2020-08-11 | 2020-12-22 | 电子科技大学 | An infusion monitoring system based on multi-sensor and wireless sensor network |
| CN112043916A (en) * | 2020-09-30 | 2020-12-08 | 河南智互智能科技有限公司 | Infusion monitoring system |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109550112A (en) * | 2019-01-22 | 2019-04-02 | 西安电子科技大学 | Infusion monitoring system based on LoRa technology |
| CN109621091A (en) * | 2019-02-15 | 2019-04-16 | 无锡识凌科技有限公司 | Intelligent transfusion monitoring system |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7154398B2 (en) * | 2003-01-06 | 2006-12-26 | Chen Thomas C H | Wireless communication and global location enabled intelligent health monitoring system |
-
2019
- 2019-06-29 CN CN201910581225.3A patent/CN110580943B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109550112A (en) * | 2019-01-22 | 2019-04-02 | 西安电子科技大学 | Infusion monitoring system based on LoRa technology |
| CN109621091A (en) * | 2019-02-15 | 2019-04-16 | 无锡识凌科技有限公司 | Intelligent transfusion monitoring system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110580943A (en) | 2019-12-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN104396865B (en) | Oestrus of sow multi-antenna and method | |
| Pranata et al. | Towards an IoT-based water quality monitoring system with brokerless pub/sub architecture | |
| CN202694093U (en) | Intelligent things network system for livestock and poultry farm | |
| CN105072581B (en) | A kind of indoor orientation method that storehouse is built based on path attenuation coefficient | |
| Parameswari et al. | RETRACTED ARTICLE: Online measurement of water quality and reporting system using prominent rule controller based on aqua care-IOT | |
| KR20200096493A (en) | Motion detection in mesh networks | |
| CN110580943B (en) | An intelligent infusion system based on LoRa communication | |
| Sung et al. | Data fusion of multi-sensor for IOT precise measurement based on improved PSO algorithms | |
| Asikainen et al. | Wireless indoor tracking of livestock for behavioral analysis | |
| Vigneswari et al. | Smart IoT cloud based livestock monitoring system: A survey | |
| CN204180708U (en) | Oestrus of sow multi-antenna | |
| Del-Valle-Soto et al. | On the MAC/Network/Energy performance evaluation of wireless sensor networks: Contrasting MPH, AODV, DSR and ZTR routing protocols | |
| Wang et al. | Design and implementation of LoRa-based wireless sensor network with embedded system for smart agricultural recycling rapid processing factory | |
| R-Moreno et al. | Efficient services management in libraries using AI and wireless techniques | |
| Abdul Haleem et al. | Wireless sensor data acquisition and control monitoring model for internet of things applications | |
| Suryawanshi et al. | Design and development of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) for water quality monitoring using Zigbee | |
| Styła et al. | A smart building resource prediction, navigation and management system supported by radio tomography and computational intelligence | |
| CN205067727U (en) | Service robot positioning system based on zigBee and RFID | |
| Lee et al. | MotesArt: Wireless sensor network for monitoring relative humidity and temperature in an art gallery | |
| Syed Taha et al. | Evaluation of LoRa Network Performance for Water Quality Monitoring Systems | |
| Chaitanya Kumar et al. | A review of smart greenhouse farming by using sensor network technology | |
| CN203135932U (en) | IoT monitoring management system | |
| Nowak et al. | Data Processing with Predictions in LoRaWAN | |
| Zhang et al. | Design of agricultural greenhouse environment monitoring system based on internet of things technology | |
| TW200925634A (en) | Method and system for wireless positioning |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20220812 |
|
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |