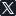Steamworks Documentation
Steam Frame Debugging
The Steam Frame runs on SteamOS, which is a gaming focused Linux distribution based on Arch. This means you have a full computer available to clearly debug what's going on with your application.
Tip: If you are developing on Windows, WinSCP is a nice tool for transferring files to/from the device.
Green means your game is making framerate. The top numbers show the game's gpu work for a single frame converted to fps (frames per second) and the texture resolution being submitted per eye. If your game is running particularly fast, it will switch to displaying milliseconds instead. The bottom row is how much time SteamVR's compositor is using per-vsync, the current gpu clock rate (in MHz) and average power draw over the past two seconds.
The bottom row is graded to show seconds.
Yellow means your game is running at half rate (each submitted frame is taking between 1 and 2 vsync intervals to finish).
Red means your game is taking more than 2 vsync intervals to finish each frame.
Pink means SteamVR's compositor gpu preemption failed for some reason.
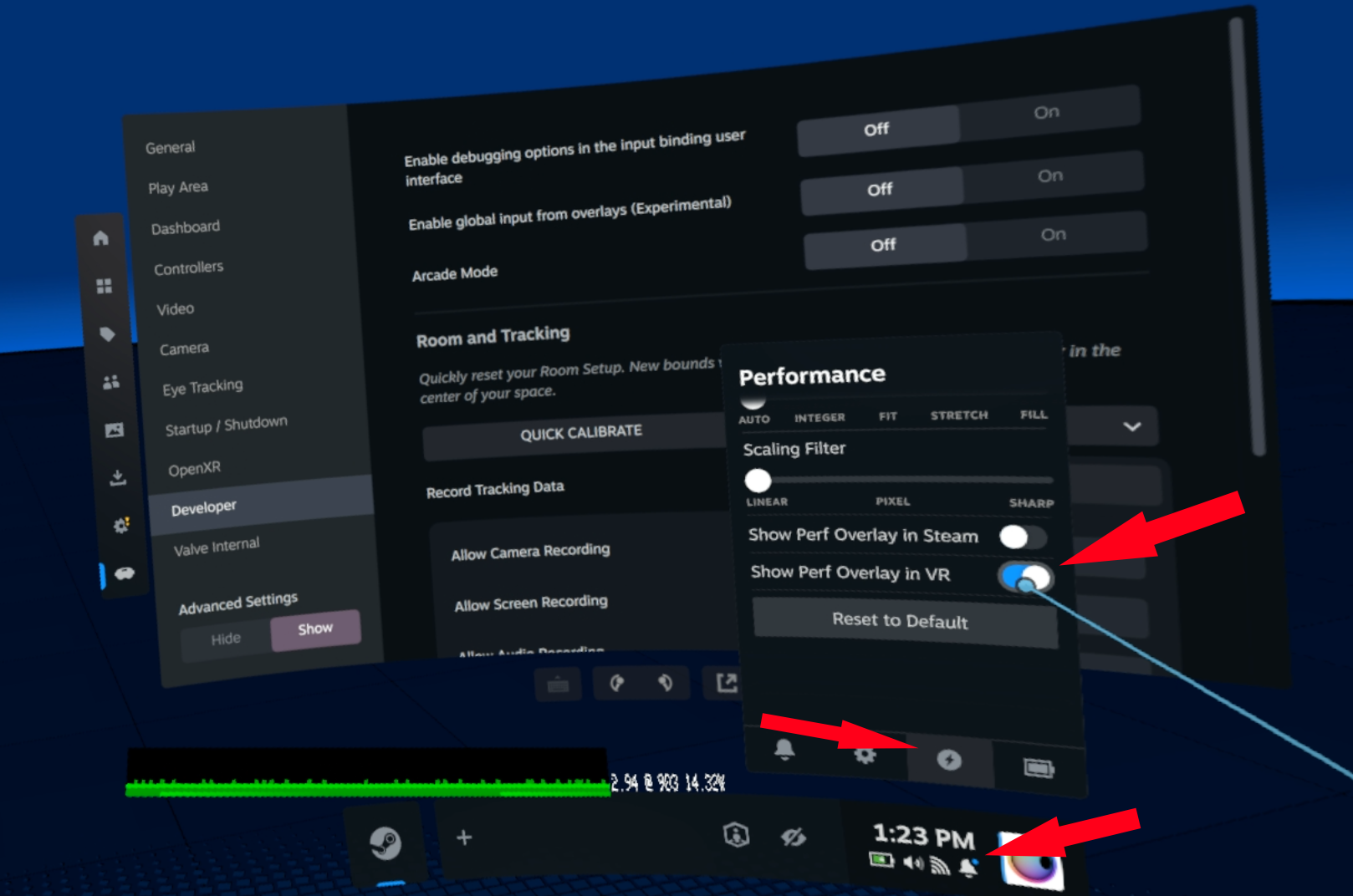
To connect, open up Remote Desktop Connection in Windows, and enter frame as the Computer.
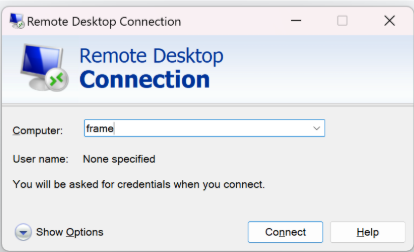
Once connected, you’ll see an XRDP login screen. Xorg should be the default session, the username is steamos and the password is whatever you had previously set in Developer Mode settings.
Once connected to headset there are a variety of helpful commands for you to use:
We recommend using the SteamOS Devkit Tool to upload your application to the device, that will create a Steam entry that you can easily add launch options to.
Before your game will show up, you will need to launch it with the renderdoc vulkan layer enabled. This can be done by setting the environment variable ENABLE_VULKAN_RENDERDOC_CAPTURE=1. You can do this in Steam by clicking the app's gear icon and editing the command line to be:
If the capture button is disabled or not working and you see the API listed as Not Presenting you may need to add EnableFrameEndMarkers=1 to your launch options as well (before %command%).
The recording has to be manually triggered to begin and end, so it's best if the issue is ongoing or if you think you can reproduce the issue without too much effort. Ideally we'd want to see tracking go from working to broken within the capture window so we can see the moment something goes wrong. If tracking recovers, it's also useful to include that recovery in the dataset.
Developer Mode
To connect to the headset via ssh, adb, or rdp you first need to enable Developer Mode as described in the Setting up your Steam Frame for development. This will allow you connect and deploy to the headset.Tip: If you are developing on Windows, WinSCP is a nice tool for transferring files to/from the device.
See the headset view remotely
You can use Steam Link to view the headset's view remotely. Using the iOS or Android app just connect to frame. On desktop you can open Steam > Settings > Remote Play and then next to frame you'll see Connect. The first time you launch Steam Link on PC it will come up full screen. Use alt+enter to switch to windowed mode. It will remember this setting on future launches.Performance Graph
You can turn on the in-headset performance graph by clicking the Clock button in the lower right hand corner of the Dashboard, then the Performance button, and at the bottom enable Show Perf Overlay In VR
Green means your game is making framerate. The top numbers show the game's gpu work for a single frame converted to fps (frames per second) and the texture resolution being submitted per eye. If your game is running particularly fast, it will switch to displaying milliseconds instead. The bottom row is how much time SteamVR's compositor is using per-vsync, the current gpu clock rate (in MHz) and average power draw over the past two seconds.
The bottom row is graded to show seconds.
Yellow means your game is running at half rate (each submitted frame is taking between 1 and 2 vsync intervals to finish).
Red means your game is taking more than 2 vsync intervals to finish each frame.
Pink means SteamVR's compositor gpu preemption failed for some reason.
Remote Desktop
After enabling Developer Mode, you can access a Linux desktop environment on Steam Frame using Remote Desktop. Windows includes an application called Remote Desktop Connection. VNC and similar programs will also work.To connect, open up Remote Desktop Connection in Windows, and enter frame as the Computer.

Once connected, you’ll see an XRDP login screen. Xorg should be the default session, the username is steamos and the password is whatever you had previously set in Developer Mode settings.

SSH
After enabling Developer Mode, you can ssh into the headset using the default user steamos and whatever password you had set under Developer Mode settings:ssh steamos@frame
Once connected to headset there are a variety of helpful commands for you to use:
- cdd - This will change your directory to a location that contains a bunch of helpful Steam Frame scripts.
- cdl - This will change your directory to the Steam Logs directory.
- lepton - Lepton is the name of our Android compatibility layer. You'll often need to specify a lepton instance, which if you're running Lepton Development from your Steam Library will be "dev". Just run "lepton" to get a description of the commands you can run. To get a color-coded logcat you can run "lepton dev logcat".
- sudo pacman - Pacman is the Arch package manager. You can search for packages with "sudo pacman -Ss packageName". You can run "sudo pacman -S packageName" to install a package.
- sudo steamos-readonly disable - By default the filesystem is read-only, so you won't be able to run things like pacman. To make it writable you can run this command. Most any changes you make will be overwritten the next time you update the OS.
Core Dumps
If a native application crashes and you get a core dump, you can use GDB to see the call stack where it crashed. After crashing, view the list of core dumps using the command:coredumpctl
This will bring up a list of core dumps available to view, along with their pid numbers. Find the one relevant to you, named after your project, and view the dump by entering the following command, replacing the number with the pid of the dump you want to view:coredumpctl debug 1234
This command will load up the dump, which might take a while. When prompted, hit enter and full symbols will be loaded. To see the stack trace where the crash occurred, enter bt from the GDB command prompt.Lepton
While working with our lightweight android translation layer, Lepton, you have a few different options available to you to help with debugging. You can ssh into the headset and get some command line options. ADB should also work like it would with any other mobile device. That means after connecting over adb you have access to:- adb logcat - Realtime steam of logs from the device
- adb shell - access the android instance's command line
- adb bugreport - Downloads a zip full of crash dumps and logs
Renderdoc with Lepton
There are two ways to work with RenderDoc. If you’re developing an Android application the standard Android workflow should be fine with the exception of connecting over adb first. If you’re connecting over wifi make sure your headset is on the same network as your PC.- On HMD: Launch Lepton Development from your Steam Library, and wait for it to finish loading.
- On PC: adb connect frame
- On PC: Open RenderDoc and in the lower left hand corner select the Android 5.x device
- On PC: adb install your app
- On PC: In RenderDoc under Launch Application select the executable path for your app.
Renderdoc for other apps
The easiest way to use RenderDoc to capture frames from Windows or Linux applications on Steam Frame is to connect from your Desktop PC using Remote Desktop and run RenderDoc there.
We recommend using the SteamOS Devkit Tool to upload your application to the device, that will create a Steam entry that you can easily add launch options to.
- Add your title with the SteamOS Devkit Client
- Remote into your Steam Frame using the instructions in the Remote Desktop section above.
- Then click the Application Launcher in the lower-left, type: renderdoc, and click to launch.
- After launching, you can right-click on the icon and pin it for future ease of access.
- From there you can File > Attach to Running Instance.When running games through Proton, you'll see three wine_preloader instances. Select the last one.
Before your game will show up, you will need to launch it with the renderdoc vulkan layer enabled. This can be done by setting the environment variable ENABLE_VULKAN_RENDERDOC_CAPTURE=1. You can do this in Steam by clicking the app's gear icon and editing the command line to be:
ENABLE_VULKAN_RENDERDOC_CAPTURE=1 %command%
If the capture button is disabled or not working and you see the API listed as Not Presenting you may need to add EnableFrameEndMarkers=1 to your launch options as well (before %command%).
ENABLE_VULKAN_RENDERDOC_CAPTURE=1 EnableFrameEndMarkers=1 %command%
Tracking Errors
If you run into serious tracking issues please let us know. Recording a tracking dataset helps us analyze what went wrong so we can address it in future updates. This is a snapshot of the entire tracking state within a window of time. This will let us replay your tracking inputs to see exactly what is happening with hmd and controller poses and test new tracking software against these exact inputs.The recording has to be manually triggered to begin and end, so it's best if the issue is ongoing or if you think you can reproduce the issue without too much effort. Ideally we'd want to see tracking go from working to broken within the capture window so we can see the moment something goes wrong. If tracking recovers, it's also useful to include that recovery in the dataset.
The dataset recording logs a wide variety of sensors on the headset but camera video, screen recording, and audio data is optional. While optional, the more data we have the more likely we will be to be able to diagnose the tracking issue you're recording data for. Additionally, if you include audio data you can talk to the recording to add context.
- Open the VR dashboard, navigate to the Steam overlay, then to VR Settings.
- Enable Advanced Settings if it's not already enabled.
- Go to the Developer settings tab and scroll down to Record Tracking Data.
- Select if you want to include camera/screen/audio data with the dataset.
- Then click START next to Record Tracking Data.
- You should see a recording icon at the top of your view. You can now close the dashboard if you'd like, then reproduce whatever tracking issue you want to capture.
- When you're finished, open the same settings window and click STOP to end the capture.
- Then to get the files you'll want to ssh into the headset: ssh steamos@frame
- Run this command to zip up the latest dataset: zip -r latestDataset.zip "$(ls -td /home/steamos/.config/openvr/config/cv/xrservice/datasets/ | head -n 1)"
- Exit ssh (just type exit)
- Download the zip from your headset into your current directory with scp: scp steamos@frame:/home/steamos/latestDataset.zip
- Then upload to your favorite file host and email us a link to the file.
Android Mesa Debug
If you want to install the mesa debug drivers to get access to lower level debugging you can do this via ssh.- ssh into your Steam Framessh steamos@frame
- Verify current Mesa versionmesa_version(should report something like Mesa 25.3.0-devel (git-8d3763730d)
- Make the filesystem writablesudo steamos-readonly disable
- Install debug mesa with pacmansudo pacman -S deckard-mesa-android-aarch64-debug