| Citation: | LI Ya, LI Haijiao, FU Yangshan, et al. Analysis of epidemiology and clinical characteristics of Lanmaoa asiatica poisoning[J]. J Clin Emerg, 2023, 24(5): 258-261, 265. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.05.007 |
Analysis of epidemiology and clinical characteristics of Lanmaoa asiatica poisoning
-
Abstract
Objective To explore the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of acute
Lanmaoa asiatica poisoning.Methods A total of 398 patients with acute
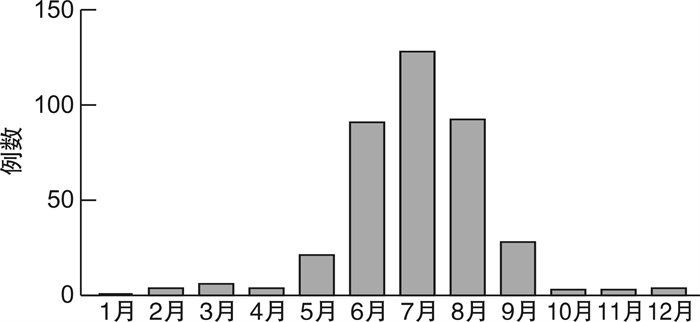
Lanmaoa asiatica poisoning admitted to the emergency department of the Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University from January 2020 to December 2021 were selected as the study objects. The relevant epidemiological and clinical data of the patients were collected and analyzed.Results ①The(93.22%), and the peak poisoning is from June to August. ②The poisoning of
Lanmaoa asiatica is mainly neuropsychiatric type 12-24 hours(82.51%), and the main symptoms are hallucinations(90.70%), delirium(35.18%), dizziness(30.65%) and mania(9.05%). ③The blood routine, liver function, renal function, myocardial enzyme, coagulation function and other indexes of patients are not significantly abnormal, and no patient died.Conclusion The peak period of
Lanmaoa asiatica poisoning is from June to August. Its first clinical symptoms are mainly neuropsychiatric symptoms. After poisoning, there is no obvious damage to the function of important organs, and the overall prognosis is good. -

-
References
[1] Li WW, Pires SM, Liu ZT, et al. Mushroom poisoning outbreaks-China, 2010-2020[J]. China CDC Wkly, 2021, 3(24): 518-522. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2021.134 [2] 蒋绍锋, 何仟, 张宏顺, 等. 毒蕈中毒病例中毒特征分析[J]. 中国医刊, 2015, 50(6): 63-67. [3] 周静, 袁媛, 郎楠, 等. 中国大陆地区蘑菇中毒事件及危害分析[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2016, 25(6)724-728. [4] 卯晓岚. 中国毒菌物种多样性及其毒素[J]. 菌物学报, 2006, 25(3): 345-363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6472.2006.03.004 [5] 刘志涛, 赵江, 李娟娟, 等. 云南省2015-2020年野生蕈中毒流行特征及趋势预测[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2021, 12(17): 7074-7079. [6] 沈秀莲, 黄甜, 贾豫晨, 等. 2005-2019年云南省毒蘑菇中毒流行病学特征及空间相关分析[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2022, 34(1): 153-158. [7] 李海蛟, 章轶哲, 刘志涛, 等. 云南蘑菇中毒事件中的毒蘑菇物种多样性[J]. 菌物学报, 2022, 41(9): 1416-1429. [8] Yin X, Yang AA, Gao JM. Mushroom toxins: chemistry and toxicology[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(18): 5053-5071. [9] 杨艳, 邵瑞飞, 陈国兵. 蘑菇中毒机制研究进展[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2020, 21(8): 675-678. [10] Wennig R, Eyer F, Schaper A, et al. Mushroom poisoning[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2020, 117(42): 701-708. [11] Thomas B. Boletus manicus heim[J]. J Psychoactive Drugs, 2003, 35(3): 393-394. [12] 代软仙, 孟强, 陈国兵. 神经精神型有毒蘑菇及其毒素研究进展[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2022, 48(8): 493-497. [13] 李毅, 于学忠. 毒蕈中毒的早期识别与治疗[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2007, 27(15): 1172-1173. [14] 中国医师协会急诊医师分会, 中国急诊专科医联体, 中国医师协会急救复苏和灾难医学专业委员会, 等. 中国蘑菇中毒诊治临床专家共识[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2019, 20(8): 583-598. [15] 姚群梅, 余成敏, 李朝宏, 等. 云南楚雄毒蕈中毒流行病学特点和救治策略的调查分析[J]. 临床医药文献电子杂志, 2017, 4(3): 574-575, 579. [16] 赵群远, 段宇珠, 陈安宝, 等. 亚稀褶黑菇中毒的临床表现研究[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2017, 18(10): 792-794. [17] 赵继芬. 65例牛肝菌中毒的诊断及治疗体会[J]. 岭南急诊医学杂志, 2015, 20(6)501-502. [18] 任成山, 王伟强, 徐梓辉, 等. 毒蕈中毒3638例临床分型的探讨[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2007, 46(3): 229-231. [19] Diaz JH. Nephrotoxic mushroom poisoning: global epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management[J]. Wilderness Environ Med, 2021, 32(4): 537-544. [20] 王毅, 邓元友. 167例急性牛肝蕈中毒的治疗[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2003, 12(9): 637-638. [21] 詹荣庭, 张明强. 蕈中毒所致精神障碍临床分析[J]. 中国民康医学, 2008, 20(20): 2383. [22] 葛丽华. 血液灌流治疗重度致幻型牛肝蕈中毒的临床疗效分析[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2022. -
Access History

- Figure 1.





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: