-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Description
通常,看源码之前会想,我们使用Vue的时候,究竟发生了什么。我们知道,每一个vue组件就是一个Vue对象。所以,应该从Vue构造函数出发。
new Vue({
el: '#app'
})构造函数的入口,在源码的src/core/instance/index.js中:
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue这个函数定义一个简单的vue构造函数,然后通过一系列方法分类注入对应功能模块的方法。其中一开始调用的this._init方法。该方法定义在initMixin之中。也就是src/core/instance/init.js中的_init方法:
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}可以先把重点放在上
...
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
...
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
...这里可以探讨一下第一个话题,也就是生命周期,如以上所见,我们看到两个钩子函数,分别是beforeCreate和created。看过官方提供的生命周期图片的同学,应该在这里会有更清晰的感受。那这里就放一下官方给的图片:
可以看到,在beforeCreate之前,官方给的描述是初始化事件&生命周期,这个描述对应的源码就是上面的 initLifecycle(vm) --> initEvents(vm) --> initRender(vm)
这几个步骤。
initLifecycle方法主要就是给vm实例添加上生命周期的相关属性,其实现如下:
export function initLifecycle (vm: Component) {
const options = vm.$options
// locate first non-abstract parent
let parent = options.parent
if (parent && !options.abstract) {
while (parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) {
parent = parent.$parent
}
parent.$children.push(vm)
}
vm.$parent = parent
vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm
vm.$children = []
vm.$refs = {}
vm._watcher = null
vm._inactive = null
vm._directInactive = false
vm._isMounted = false
vm._isDestroyed = false
vm._isBeingDestroyed = false
}initEvent方法是绑定vue提供的事件接口$once, $emit, $on, $off。
而在beforeCreate钩子之后,才真正执行注入和初始化数据的操作。这个时候,我们可以提出一个疑问:
beforeCreate钩子里面能拿到prop和data吗?
我想看了上面的图或者代码,可以知道initState是在beforeCreate后面。
同时,也可以提出第二个疑问:
vue依赖收集发生在哪个阶段?
关于依赖收集应该是第二个话题,也就是vue双向绑定和监听的原理。
响应式原理
接着上面的代码走,应该看initState了,initState涉及到响应式。看过文章应该大多数都知道,vue采用Object.defineProperty方式实现响应式。但是要具体搞懂整个流程走向可远不止于此。对于defineProperty的使用不是很了解自行科普。这里不花时间接受这个属性。这一切发生在上面的initState方法里面。
同时,先不直接看代码流程,先看官方给的图。官方也给了响应式数据流向图。
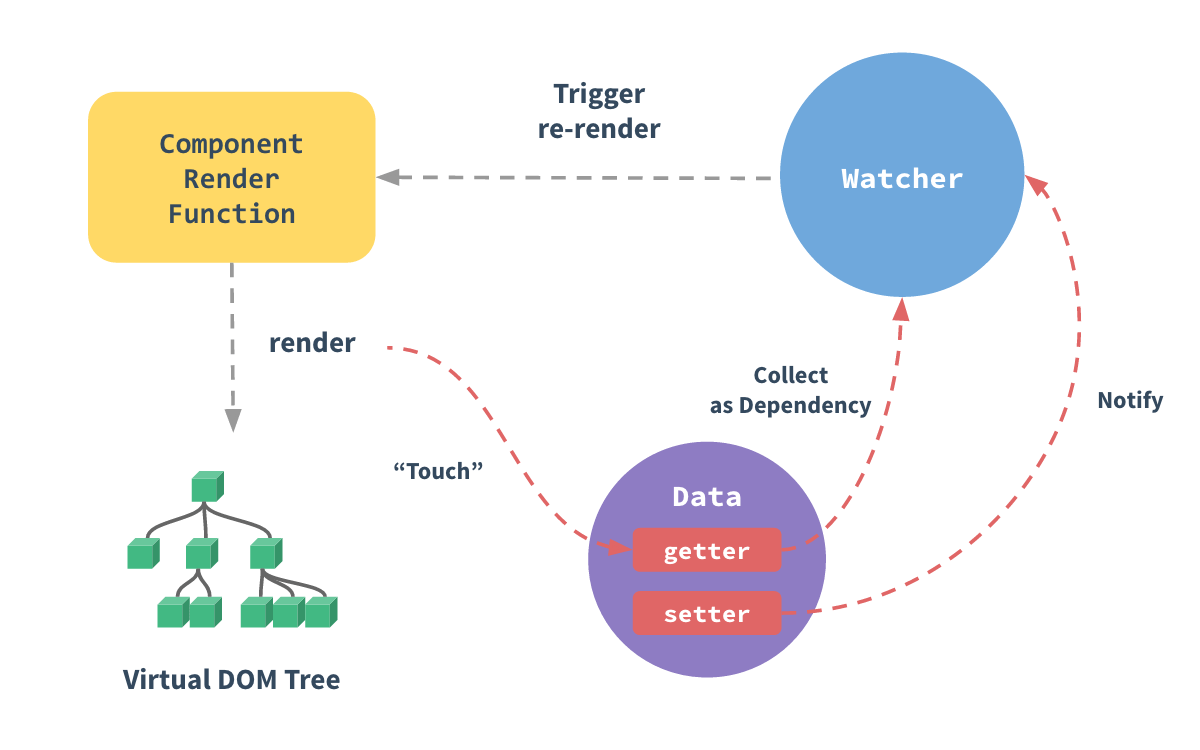
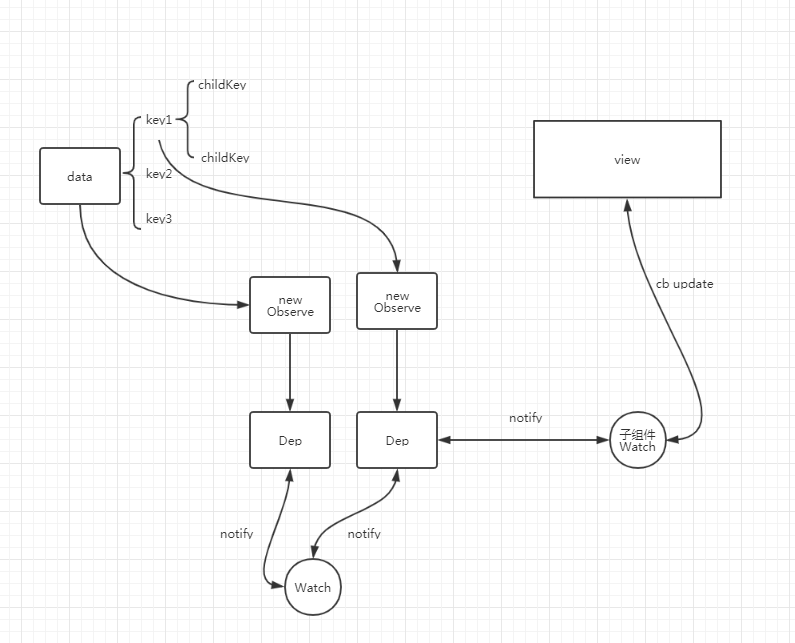
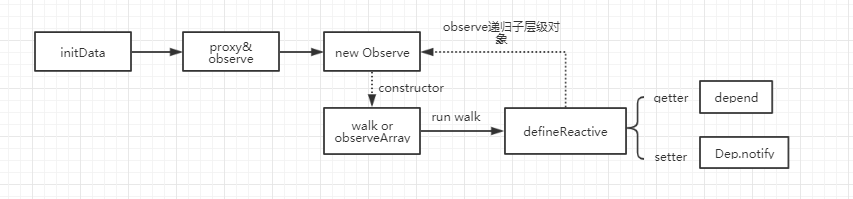
看上图,也就是说initState中会调用initData初始化用户定义的data数据,
- 通过proxy方法会给vm对象(new Vue产生的实例)挂上对应data上的所有属性。
- 之后调用observe(data)监听data上的数据。observe是判断是否有Observe对象,如果没有则创建。
- Observe构造函数中,会判断data是对象还是数组,如果是对象直接调用walk函数,如果是数组循环调用walk函数。walk函数会循环对象的key对每一个key,value调用defineReactvive函数。
- defineReactive函数就是调用defineProperty初始化访问器属性getter,setter。
- 在getter中会定义依赖收集的方法。在setter中会调用dep.notify更新所有watch相应数据。
这里比较难理解是依赖收集的实现方式,就是收集的时机。收集是在Watch对象构造函数中构造时候收集的,至于什么时候构造Watch对象,有以下几个场景:
- 组件挂载前,会调用new Watch去执行,并且在Watch中会回调render函数,在render时候会做收集
- 计算属性在定义时候
- watch的属性定义时候
在initData中就是步骤1
到这里,initData的代码就整理完了,接下来贴上真正的源码验证我上面所说的。
首先initState方法如下:
export function initState (vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm)
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}然后是initData
function initData (vm: Component) {
let data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {}
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {}
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
'data functions should return an object:\n' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm
)
}
// proxy data on instance
const keys = Object.keys(data)
const props = vm.$options.props
const methods = vm.$options.methods
let i = keys.length
while (i--) {
const key = keys[i]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a data property.`,
vm
)
}
}
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`The data property "${key}" is already declared as a prop. ` +
`Use prop default value instead.`,
vm
)
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
proxy(vm, `_data`, key)
}
}
// observe data
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
}其实只需要看proxy和observe其他的只是对做data处理。proxy是循环,这样可以通过this.key的方式在vue中使用data数据。
observe代码:
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value)
}
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
}判断是不是有__ob__属性,没有创建Observer对象。
class Observer定义如下:
export class Observer {
value: any;
dep: Dep;
vmCount: number; // number of vms that have this object as root $data
constructor (value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this)
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods)
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
}
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
this.walk(value)
}
}
/**
* Walk through all properties and convert them into
* getter/setters. This method should only be called when
* value type is Object.
*/
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}
/**
* Observe a list of Array items.
*/
observeArray (items: Array<any>) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}判断是数组还是对象数组的话循环调用observe然后在调用walk,对象直接调用walk,总之就是调用walk。walk调用defineReactive。
接下来看看defineReactive方法定义:
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
const dep = new Dep()
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key)
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get
const setter = property && property.set
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) return
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
})
}关于Dep的定义如下:
export default class Dep {
static target: ?Watcher;
id: number;
subs: Array<Watcher>;
constructor () {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = []
}
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
notify () {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
const subs = this.subs.slice()
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
// subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async
// we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct
// order
subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
}
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
}
// The current target watcher being evaluated.
// This is globally unique because only one watcher
// can be evaluated at a time.
Dep.target = null
const targetStack = []
export function pushTarget (target: ?Watcher) {
targetStack.push(target)
Dep.target = target
}
export function popTarget () {
targetStack.pop()
Dep.target = targetStack[targetStack.length - 1]
}关于watch的定义是:
export default class Watcher {
vm: Component;
expression: string;
cb: Function;
id: number;
deep: boolean;
user: boolean;
lazy: boolean;
sync: boolean;
dirty: boolean;
active: boolean;
deps: Array<Dep>;
newDeps: Array<Dep>;
depIds: SimpleSet;
newDepIds: SimpleSet;
before: ?Function;
getter: Function;
value: any;
constructor (
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: Function,
options?: ?Object,
isRenderWatcher?: boolean
) {
this.vm = vm
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this
}
vm._watchers.push(this)
// options
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep
this.user = !!options.user
this.lazy = !!options.lazy
this.sync = !!options.sync
this.before = options.before
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false
}
this.cb = cb
this.id = ++uid // uid for batching
this.active = true
this.dirty = this.lazy // for lazy watchers
this.deps = []
this.newDeps = []
this.depIds = new Set()
this.newDepIds = new Set()
this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
? expOrFn.toString()
: ''
// parse expression for getter
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn)
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = noop
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Failed watching path: "${expOrFn}" ` +
'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' +
'For full control, use a function instead.',
vm
)
}
}
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get()
}
/**
* Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies.
*/
get () {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}
/**
* Add a dependency to this directive.
*/
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
/**
* Clean up for dependency collection.
*/
cleanupDeps () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
const dep = this.deps[i]
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
dep.removeSub(this)
}
}
let tmp = this.depIds
this.depIds = this.newDepIds
this.newDepIds = tmp
this.newDepIds.clear()
tmp = this.deps
this.deps = this.newDeps
this.newDeps = tmp
this.newDeps.length = 0
}
/**
* Subscriber interface.
* Will be called when a dependency changes.
*/
update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
/**
* Scheduler job interface.
* Will be called by the scheduler.
*/
run () {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
try {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, this.vm, `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
}
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}
/**
* Evaluate the value of the watcher.
* This only gets called for lazy watchers.
*/
evaluate () {
this.value = this.get()
this.dirty = false
}
/**
* Depend on all deps collected by this watcher.
*/
depend () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
/**
* Remove self from all dependencies' subscriber list.
*/
teardown () {
if (this.active) {
// remove self from vm's watcher list
// this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it
// if the vm is being destroyed.
if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
remove(this.vm._watchers, this)
}
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].removeSub(this)
}
this.active = false
}
}
}这个方法比较多,而且确实不好理解,因为定义为访问器属性,真正getter setter会在后面某个时间运行,比如getter是在使用时候执行。setter时候是在修改执行。这里需要重点关注的是,注意是重点关注,是Dep.target的判断这个值默认是null,什么时候会赋值后面继续看。dep.depend就是依赖收集的过程,其包括两个步骤:
- 调用Dep.target.addDep (也就是当前Watch的dep数组里面会添加上这个dep)
- watch里面又会回调Dep的addSub方法将当前watch添加到Dep的subs里面
所以上面图片反映的是,每个Dep对象会有多个watch,每个watch也会对应多个Dep。
这里需要结合生命周期重新屡一下思路:
- 在beforeCreate之后,created之前,执行了initState初始化了数据,
- 于是走了上面流程定义了data和其访问器属性(即getter setter)。
- 然后调用created钩子,执行mount函数。
- 在mount函数里面,调用beforeMount钩子,然后创建Watch,
- Watch代码在上面。在Watch里面会this.getter.call(vm, vm)执行参数2,该参数就是传入的updateComponent函数。
- 执行render过程,触发data的getter。getter里面做依赖收集。将依赖的属性添加到subs数组。后续数据更新就会触发cb回调重新渲染视图
- Watch创建完毕
- 执行mouted
至此依赖收集过程就讲完了,后续有空再看render过程。