Викисклад:Типы файлов
Викисклад принимает только «бесплатный контент». Аналогично, разрешены ТОЛЬКО бесплатные форматы файлов.
Файлы в форматах, обременённые патентами, не принимаются на Викискладе. Список разрешённых форматов файлов см. в разделах ниже. Примерами форматов файлов, обременённых патентами, являются AAC, WMA и большинство кодеков AVI. Наша миссия требует, чтобы материалы были свободно распространяемы для всех. Форматы, обременённые патентами, не соответствуют этому стандарту.
Файлы в несвободных и неподдерживаемых открытых форматах должны быть преобразованы в поддерживаемый свободный формат перед загрузкой. К счастью, это обычно несложно, но может занять много времени (в зависимости от формата и желаемого выходного качества).
Изображения
На Викискладе мы рекомендуем следующие типы файлов: SVG, PNG и JPEG.
BMP-файлы недопустимы для Викисклада. Их можно без потерь преобразовать в PNG, и размер файла всегда будет меньше. Пользователи Windows могут конвертировать BMP в PNG с помощью встроенного редактора Microsoft Paint, просто открыв файл и сохранив его как PNG. Paint поддерживает PNG, начиная как минимум с Windows XP. Пользователи Linux могут использовать утилиту командной строки FFmpeg: ffmpeg -i "input filename.bmp" "output filename.png".
Размер и масштабирование
См. также: Викисклад:Максимальный размер файла
- Обратите внимание, что с момента написания текста ниже было установлено новое программное обеспечение для изменения размера PNG.
К сожалению, система масштабирования изображений всё ещё ограничена. В настоящее время миниатюры (PNG, GIF, JPEG) генерируются в том же формате, что и исходное изображение, и всегда имеют 24-битную цветовую глубину (за исключением GIF-изображения, в котором итоговое изображение будет иметь 256 цветов). Это означает, что масштабирование PNG-изображений создаёт довольно большие файлы, даже если исходное изображение содержало палитру или было в оттенках серого. Это также означает, что если вы хотите загрузить PNG-файл фотографии без потерь для редактирования и архивирования, но хотите использовать JPEG-миниатюры в статьях, вам придётся вручную загружать полноразмерную JPEG-версию.
Обратите внимание, что масштабирование изображений может завершиться неудачей, если изображение очень большое и его рендеринг занимает слишком много времени или памяти (в этом случае либо масштабированное изображение не отображается, либо в браузер передается полное изображение, что часто приводит к его зависанию). Для GIF-изображений действует жёсткое ограничение в 1,000 мегапикселей.[Note 1] Большие JPEG-файлы обычно проблематичны только если они сохранены в прогрессивном режиме. Вместо этого используйте базовый режим (см. Progressive JPEGs).
Самое высокое разрешение
Тем не менее, пожалуйста, помогите обеспечить широкое повторное использование материалов Викисклада, в том числе в печатных СМИ, загружая фотоизображения в высоком разрешении. В случаях, когда версия с самым высоким разрешением имеет проблемы, описанные выше, можно загрузить версию с меньшим разрешением под другим именем (указав в описании изображение с более высоким разрешением) или как новую версию файла. Подробнее см. Commons:Почему нам нужны файлы в высоком разрешении. С другой стороны, Special:AbuseFilter/153 ограничивает кросс-вики-загрузку JPG-файлов меньшего размера (<50 000 байт или <2 000 000 пикселей) новыми участниками.
SVG
- См. также Справка:SVG и Wikipedia: Graphic Lab/Resources/SVG.
SVG — основанный на XML формат векторной графики, который можно масштабировать без размытия или пикселизации. Он легко редактируется и обычно создаёт файлы достаточно небольшого размера (см. File:Bitmap VS SVG.svg). Формат SVG предпочтителен для создания диаграмм, флагов и т. д., а PNG хорошо подходит для отсканированных изображений и фотографий печатного качества. См. Справка:SVG.
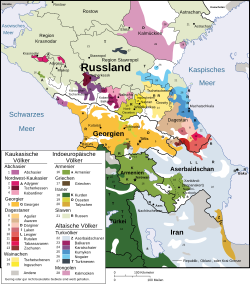
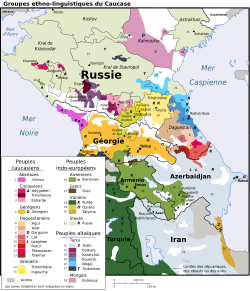
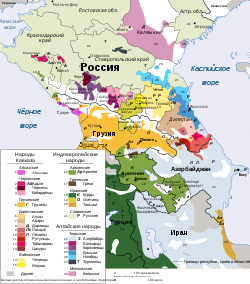
SVG хорошо подходит для диаграмм, графиков, иллюстраций, карт и любой графики, требующей подписей. SVG может хранить подписи в виде текстовых строк, поэтому SVG-графику можно переводить на другие языки, редактируя текстовые строки. Например, карта File:Caucasus-ethnic en.svg ниже переведена на несколько языков. Сравните качество изображения SVG-карт разных размеров по сравнению с картой в JPG. (Изображения, представленные ниже, на самом деле имеют формат PNG. SVG-изображения в Википедии не отображаются в браузерах. Вместо этого MediaWiki преобразует SVG-изображение в PNG-изображение и отображает его в формате PNG.)
-
немецкий
-
английский (JPEG)
-
английский
-
испанский
-
французский
-
русский
-
польский
PNG
PNG — формат сжатия изображений без потерь (поддерживает альфа-прозрачность), что означает сохранение точного цвета пикселя при сохранении и может использоваться для любых рисунков/диаграмм, недоступных в формате SVG (SVG предпочтительнее для создания диаграмм и т. д.). Формат PNG подходит практически для всего, кроме фотографий, сделанных цифровыми камерами. PNG лучше подходит для сканированной графики (хотя и с оговоркой — см. примечание о резкости ниже) и изображений с низкой глубиной цвета. Всё это при меньшем размере и более высоком качестве по сравнению с JPEG.
В Википедии (и всех других инсталляциях MediaWiki, как обсуждалось в phab:T192744) миниатюры PNG не имеют повышенной резкости, в отличие от миниатюр JPEG. Для более сложных изображений, таких как фотографии, гравюры и т.д., PNG отображает миниатюру худшего качества. Однако основная проблема JPEG заключается в том, что, будучи форматом сжатия с потерями, его невозможно многократно редактировать даже при наилучших настройках качества. Поэтому, даже если миниатюра PNG некачественная, рекомендуется загрузить также PNG и связать копии PNG и JPEG с помощью шаблона {{PNG with JPEG version}}. Исключением являются случаи, когда исходное изображение уже в формате JPEG; в таких случаях нет смысла предоставлять копию PNG. Однако, если вы редактируете JPEG, неплохо сохранить копию PNG перед закрытием программы, в которой он редактировался; это даст копию, которую другой человек сможет редактировать без дальнейшего ухудшения качества. Также для более простых изображений см. Help:How to reduce colors for saving a JPEG as PNG — простые изображения обычно имеют меньший размер файла, чем JPEG, если изображение относительно простое.
Exif-данные
Очень важно помнить, что в PNG-файлах нет собственных EXIF-данных,[Note 2] так что если вы хотите загрузить фотографию, снятую в RAW-формате, сохраните её из RAW-файла в JPEG и, если хотите, загрузите из RAW-файла также и PNG. Но если вы хотите отретушировать фотографию, сохранив EXIF-данные, профессиональный способ для этого — отредактировать исходный файл необработанного изображения или версию PNG, сохранить изображение в формате JPEG и скопировать EXIF-данные из файла необработанного изображения в конечный JPEG-файл. Не существует единого стандартного способа сделать это правильно. Другие участники помогут вам, если ваш инструмент выдает что-то очень неправильное (UTF-8 за пределами фрагмента iTXT или что-то подобное).

JPEG
Формат JPEG (также JPG) подходит для фотографий, особенно если они изначально созданы в JPEG. Он использует «сжатие с потерями», жертвуя точностью ради меньшего размера файла.
If you have a choice of file formats in which to save a graphic, scan, or other such thing, save it as PNG (or save it as another lossless format, such as TIFF, and convert to PNG), and upload it as such. However, if the original file is in JPEG, it generally makes no sense to convert it to PNG: converting a lossy compression into a “lossless” format doesn't buy you anything since the “loss” already occurred in the original, and doing so will only increase the file size (any edits, however, should probably be saved as PNG as well as JPEG). An exception is high resolution JPEGs that have no visible compression artifacts. Conversion to PNG will avoid the thumbnails having additional compression artifacts.
Другим исключением является использование инструментов для устранения JPEG-артефактов и последующее сохранение в формате PNG. Подробнее об этом см. на странице Help:JPEG#Fixing JPEG artifacts.
Note that currently, JPEG thumbnails receive extra sharpening, while PNG thumbnails don't. Hence, uploading in both formats may be a good idea if the PNG thumbnails look a bit blurry. Use {{JPEG version of PNG}} on the JPEG versions of a PNG flagged as {{PNG with JPEG version}}.
PNG is a lossless full-color format. JPEG is always a lossy format, even at the highest quality settings. Lossless formats do not degrade after being saved repeatedly, but lossy ones do; hence, having a lossless version of the file allows the file to be tweaked for various purposes—cropping, levels adjustment, and so on—without a loss in quality.
- See also Help:JPEG, Справка:Сканирование[Note 3]
GIF


PNG is almost always superior to GIF for still images (smaller size, more colors, better transparency). If you are creating or editing a graphic (not a photograph), and have a choice of file formats to save it in, the preferences for Wikipedia/Wikimedia use is SVG first, then PNG. Never save an image with more than 256 colors in the GIF format. GIF always saves images as 256 colors or less. Converting higher-color images to the GIF format will degrade those images.
Editing of GIF files can be unwieldy because GIF only supports an 8-bit palette and most filters only function on the full palette. And PNG supports 8-bit transparency (alpha channel) in contrast to GIF's 1-bit transparency. There are also certain idiosyncracies in GIF resizing; notably, when a GIF with background transparency is thumbnailed, the transparent area eats into the non-transparent area, which can create problems.
If you find some quality freely licensed GIF graphics, diagrams, charts, maps, illustrations, etc. that you think would be useful for Wikipedia or one of its sister projects, feel free to upload them to Commons as-is. You or others can convert them to SVG format later if need be.
- См. Commons:Chart and graph resources для получения информации об инструментах и помощи.
Анимированный GIF
GIF is a lossless, 8-bit color format (maximum of 256 colors) and should be used mainly for animated images on Wikimedia Commons. For animated images GIF uses lossless compression of images up to 256 colors per frame.
Animated GIF files sometimes have problems when thumbnailed. If you find your animation corrupted or distorted when scaled down, try re-saving it with every frame the same size: A common optimization method in animated gif crunchers is to write variable-sized frames, sometimes labeled as: “Save only the portions of frames that have changed”. Wikimedia’s current version of ImageMagick does not seem to support this. There is currently a 100 megapixel restriction in our software; please see the description in Category:Animated GIF files affected by MediaWiki restrictions for details.
If the image is sufficiently long (more than 10 seconds), considering using one of the video formats below: video can be paused and rewinded. FFmpeg may be used to convert a GIF to video.
Inline animations should be used sparingly; a static image with a link to the animation is preferred unless the animation has a very small file size. Keep in mind the problems with print compatibility mentioned above.
TIFF
Only some TIFF files can, at this time, be displayed in resized (thumbnailed) form within Wikipedia or on Commons, and TIFF files are not supported by most Internet browsers. They are an archival format, and should never be used for images intended to be displayed.
TIFF generally serves as a lossless format, similar to PNG, but with much less compression. However, its standard compression algorithm is very fast to apply (which was a benefit on older computers) and most scanner software supports TIFF, making it a popular choice for archives.
PNG is not supported by most scanner software, but files saved in PNG can generally be made much smaller than TIFF files. For instance, one 33 MB TIFF reduced to 17 MB when saved as a PNG.
Overall, PNG is a preferred format; however, the ability to upload TIFF files is offered as a courtesy. For instance, if you were batch scanning files in order to upload them to Commons for others to edit and prepare, you would want to use a lossless format (editing a non-lossless format causes an increase in artifacts every time it is saved). Your scanner software may not support saving directly to PNG, but allow TIFF. In such cases, uploading the image as a TIFF file is acceptable, as it helps you donate material to Commons much more easily (in that specific case, it would be appropriate to inform the regulars on the Village Pump noticeboard so that your batch upload can be prepared for more widespread use and possibly to discuss things beforehand briefly). There are many image editors (free and commercial) that can handle conversion from TIFF to other formats. See: en:Comparison of raster graphics editors #File support.
The statements above apply to the vast majority of TIFF files; however, note that TIFF is a somewhat odd format – the specifications are loose, and can, in theory, support a wide variety of compression schemes and file storage (though most programs that open TIFFs only recognise the most common). This makes it difficult to make definite statements about TIFFs: For instance, TIFFs can contain JPEGs, which are not a lossless format. Generally, only TIFFs of the standard types should be uploaded to Commons.
WebP
Формат изображений WebP поддерживается на Викискладе. Он поддерживает как сжатие изображений с потерями на основе VP8, так и сжатие изображений без потерь на основе нового алгоритма. Сжатия без потерь у него лучше, чем у PNG.
Commons do not support generating thumbnail of WebP image in WebP format. The preview is still in JPEG format. In addition, thumbnail generation for animated WebP is not supported. The preview of WebP animations will be blank, making it unable to show the animation on Wikipedia.
XCF
XCF can be useful if you are working on an image with GIMP. Unlike PNG and similar files, XCF files support text and multiple layers. It may be useful to upload the XCF file, so that other editors can continue working with it directly, while retaining the layering information. Please note that a thumbnail of a XCF can only be generated by the MediaWiki software if the file format is compatible with GIMP 2.6 or 2.8 and the color mode is RGB or grayscale. In other words, images with indexed colors are not supported by the MediaWiki thumbnailer; neither are files created with GIMP 2.10 (see T196054).
Звук
На Викискладе можно загрузить следующие типы файлов: MP3, Ogg (с использованием кодеков FLAC, Speex, Opus или Vorbis), WebM (с использованием Vorbis), FLAC, WAVE или MIDI.
Non-free formats and lesser-known free formats must be converted before uploading—there is currently no legitimate way to store pristine original data for conversion to future formats or for use when patents expire, even if the license of a given work requires distributing such pristine original data (as is often the case for works distributed under the GNU Free Documentation License or other copyleft licenses).
The Commons does not accept tracker formats, even formats written by free trackers. Nor does it accept sound fonts for use with MIDI files, even sound fonts designed for use with free MIDI players. If it is important that a musical passage be heard with specific instrument definitions that General MIDI does not provide for, and the license allows it, use your tracker software to render the passage to RIFF WAVE, and then encode it to Ogg Vorbis.
As of June 2023, most browsers can play MP3, Ogg Vorbis, and Opus, but not MIDI, FLAC or Speex. FLAC and Speex are automatically converted to Vorbis and MP3 transcodes for playback on browsers after upload.
MP3
MP3 — широко поддерживаемый аудиоформат, который настоятельно рекомендуется использовать, если не удаётся найти ogg-версию или версию со сжатием без потерь. В настоящее время Викисклад принимает MP3-файлы только от участников с правами автопатрулируемых или выше, поскольку сообщество не может отслеживать нарушения авторских прав.
MIDI
MIDI-файлы принимаются, но поддерживаются не очень хорошо. Расширение файла должно быть .mid.
Ogg (аудио)
Opus is the preferred audio codec for the Ogg container. Please use the file type opus or oga to upload audio files in Ogg Opus format.[Note 4]
Opus is supported by MediaWiki (phab:T42193, phab:T53313) since 2014. The format has excellent quality and low algorithmic delay. It automatically switches between speech and music-optimized modes and is able to combine the two. FLAC is for general audio and is lossless (quality is preserved), but current file size caps prevent its use for anything but short clips. In most cases, Opus should be used, using Xiph recommended settings.[Note 5]
Существующее аудио в других свободных кодеках (таких как Speex и Vorbis), но присутствующее в Ogg-контейнере, не следует конвертировать в Opus или FLAC, чтобы избежать потерь генерации.
Note that with FLAC, a native container format exists (see below).
If your output file has the extension .flac, it is likely using the native container format.
If you like to embed it into an ogg container, this can be done with FFmpeg using the command line ffmpeg -i InputFile.ext -acodec flac out.oga or flac ./input.wav -8 --ogg -f ./output.oga.[Note 4] (Doing so is neither required nor recommended.)
It is also useless to put data in a non-free format into a free container like Ogg: you get a file, which, while requiring that a player support the free container, still requires that it support the non-free codec.
WebM (аудио)
The WebM container can hold audio (Vorbis or Opus), with or without accompanying video.
FLAC
The Free Lossless Audio Codec is supported with or without encapsulation into ogg-containers. TimedMediaHandler will automatically offer transcoded variants in ogg format. File extension without encapsulation: .flac. (The related phab:T51505 was resolved in 2013 and closed in 2014.)
WAVE
Wave containers usually contain uncompressed, lossless audio (PCM).
If possible, please convert to FLAC before uploading. File extension: .wav.
Видео
Videos must be WebM files (.webm extension), Ogg files using the Theora video coding format (with a .ogv extension[Note 4]), or MPEG-1/MPEG-2 files (.mpg and .mpeg extension). Non-free formats must be converted before uploading. See Commons:Video – Uploading a video for instructions.
See Video2Commons for a fast and easy tool.
The recommendation of MDN Web Docs is WebM containing VP9 video with Opus audio. Can I use reports that some 92% of 2024 users are able to directly use this combination, much more than Ogg Theora (~8%).[Note 6]
WebM (видео)
WebM supports the VP8, VP9, and AV1 video coding formats, and the Vorbis and Opus audio coding formats. The container format WebM is a subset of Matroska.
VP8 is a lossy compression format which has better quality than Theora does. Of course, there is no need to transcode existing Theora videos to VP8, because it won't fix the damage by a prior more lossy compression. While WebM is more widely supported by browsers, such compatibility issues are to be fixed by automatic transcoding in MediaWiki software, not by manual re-upload.
VP9 is a successor to VP8, having better compression efficiency.
AV1 is a successor to VP9 and offers better compression efficiency. It's slated to have much wider industry support both in software and hardware than previous free video formats. As of 2025, 83% (93.55% with partial support) of users are able to play this format; the main blocker is Safari, which only supports AV1 on devices with a hardware decoder.
Ogg Theora (видео)
Theora is a lossy video coding format released in 2004. It is based on VP3 in the line leading to Flash VP6/VP7 and WebM VP8/VP9. (Note: Most software mentioned at Викисклад:Программное обеспечение should also be able to play Ogg Vorbis audio.)
As of 2023. Theora is poorly supported by modern browsers' HTML5 video players. Avoid converting to this format.
MPEG-1 (video)
MPEG-1 is the VCD standard, which includes MP2 and MP1 standards, for lossy compression of video and audio released in 1993. It was designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to about 1.5 Mbit/s (26:1 and 6:1 compression ratios respectively) without excessive quality loss.
MPEG-2 (video)
MPEG-2 is the DVD standard, which includes MP2, for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information" first released in 1996. It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission bandwidth. Both of MPEG-2 and MPEG-1 are standards of digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting (DAB).
Текстовые форматы
Отсканированные текстовые документы (DjVu, PDF)

Although Commons does not generally host documents, there are valid reasons to upload them here (such as archival versions for transcription use on Wikisource).
- See Help:DjVu to get help about DjVu and PDF files.
- Documents in PDF format are allowed. Usage as graphic is not recommended, as you can see on the right example, which is a clear vector graphic. For allowable reasons of PDF and DjVu format, see Project Scope, PDF and DjVu formats.
Note that any page from a PDF currently gets rendered as JPG by thumbnails, but this could as well be rendered as PNG. This only depends on the implementation of the PDF renderer used on the image thumbnail server and it is not a limitation of the PDF format vs. DejaVu. The only limitation is the existence of various proprietary extensions of the PDF format which could sometimes require a specific PDF viewer. PDF files in Commons should not depend on these extensions and should use only the core specifications, used by the thumbnail renderer of Commons. The issue may exist only when PDFs are downloaded in native format from the "Media:" namespace instead of being rendered as a single image from a selectable page number in the PDF (because these extensions may embed some active scripting, form handlers, and active links to external sites).
For single image rendering, PDF files rendered with the core PDF profile (from its standard specifications) are functionally equivalent to DejaVu files, but typically render photographs and graphics with higher fidelity and more accurate color profiles than DejaVu files which use a more basic model. PDFs also offer better quality in some cases as they can embed scalable vector graphics, instead of just highly compressed bitmaps at a fixed resolution. So the difference is basically on the compression level for bitmaps: for scanned text documents, DejaVu is often smaller than PDF, but this does not make a difference when these files are rendered as a single bitmap image instead of being downloaded.
For documents containing colorful graphics and photos, PDFs frequently offer better fidelity and accuracy. However, image thumbnail renderers currently used by Commons do not render them clearly because they generate JPEG thumbnails instead of more accurate PNG thumbnails: this could change in the future when an agreement is reached at phab:T38597.
Noting that due to many copyright infringements and out of scope files being uploaded, we do not allow new users to upload PDF files.
- See also Справка:Сканирование for advice on scanning non-text items.
TimedText
TimedText is a custom Commons namespace to hold “Timed Text”, also termed subtitles, closed captioning and closed caption text. The contents are plain text with no markup whatsoever.
Файлы данных
No database file types are currently supported as a file type for uploading to Commons. (See the list of unsupported file types below.)
However, tabular data can be stored in the dedicated Data: namespace. For example, data in this namespace can include:
- Map data, allowing users to store GeoJSON data.
- Tabular data, allowing users to create CSV-like tables of data.
This also supports the creation of dynamic text (via Lua modules) and graphs using data in JSON format.
Data files in Commons have to be set under one of these license: CC0 1.0, CC BY-1.0, CC BY-2.0, CC BY-2.5, CC BY-3.0, CC BY-4.0, CC BY-4.0+, CC BY-SA-1.0, CC BY-SA-2.0, CC BY-SA-2.5, CC BY-SA-3.0, CC BY-SA-4.0, CC BY-SA-4.0+, ODbL-1.0, dl-de-zero-2.0, or dl-de-by-2.0.
Feel free to experiment by creating pages with the Data:Sandbox/<username>/ prefix. For now, page content can only be edited in the raw JSON format unless, each field have the type 'number' or 'string'. To categorise Data files, categories can only be added to their corresponding Data talk pages.
Данные карт
- Подробнее на странице Данные для географических карт.
Map data allows users to store GeoJSON data, similar to images. Other wikis may use this data to draw on top of the maps, together with other map customizations, using Kartographer.
To create a new map data, create a new page in the Data: namespace with the .map suffix, such as Data:Sandbox/Example user/Example.map.
- реальный пример: Data:NewYork.map
Табличные данные
- Подробнее на странице Табличные данные.
Tabular data allows users to create CSV-like tables of data, and use them from other wikis to create automatic tables, lists, maps and charts.
To create a new table, create a new page in the Data: namespace with a .tab suffix, such as Data:Sandbox/Example user/Example.tab.
- real example: Data:Ncei.noaa.gov/weather/New York City.tab
Форматы для дизайна и САПР
- 3D structures
- STL for 3D files, the file format most commonly used for 3D-printing. Other 3D formats and Other CAD_file_formats are unsupported. See also mw:Help:Extension:3D.
Другие форматы
- Chemical and biological molecular structures
- None supported yet. See unsupported file types below.
- Map routes and GPS data
- See Map data. See also unsupported file types below.
Запрос поддержки новых типов файлов
As of 2021, there is no standard process for requesting support for new file types. Discussion on MediaWiki.org
The MediaWiki manual includes a description of how to add support for a new file type, which mentions some considerations when adding support on Wikimedia websites.
As a first step, read that manual page + file a ticket requesting support linking to this umbrella tracking ticket: Multimedia file format support (tracking). You can find examples of past requests, open and closed, linked to it already; and a summary below of past requests that remain unsupported.
Неподдерживаемые типы файлов
Неподдерживаемые типы свободных файлов
Requested at least once, but not currently supported; help needed to support these. :-)
- Any format for 3D except STL (which is already supported)
- For supporting full-colour 3D models, see phab:T246901
- See also Commons:Requests for comment/Hosting files for 3D models.
- Any format for data
- (CSV, ODF ODB, etc.) – phab:T45151
- Any format for chemical or biological molecules
- Chemical Markup Language (CML) – phab:T18491
- MOL and SDF – see Extension:MolHandler phab:T66548, phab:T69993
- Protein Data Bank (PDB) – see Extension:PDBHandler – phab:T46660
- Any map route/GPS format
- KML Keyhole Markup Language – phab:T28059, phab:T57549
- GPS eXchange Format – phab:T55023, phab:T57549
- OSM OpenStreetMap export format – phab:T27139
- Most open document formats
- Scribus – phab:T20845
- OpenDocument (ODT, ODS, ODP, etc.) – phab:T4089 – rejected in its current support in July 2014
- EPUB – phab:T19858
- Comic book archive
- Image formats
- Digital Negative (DNG) – phab:T21153
- HDRI high dynamic range formats (e.g. OpenEXR) – phab:T19505
- ICO – has volunteer, needs task number (previous discussion)
- JPEG 2000 (JP2/JPX) – phab:T161934, phab:T13871 & phab:T20803[Note 7][Note 8]
- Better Portable Graphics (BPG) – phab:T84943
- Stereoscopic image format(.JPS and .MPO) – phab:T40416
- AVIF – phab:T257719
- JPEG XL (JXL) - phab:T270855
- Audio/video formats
- ALAC (Apple) – phab:T34104
- MKV container format – phab:T32653#347603 (WebM is a subset of Matroska and is supported on Commons, but full Matroska support does not appear to be planned)
- Diagram formats
- Dia diagram format – phab:T26252
- Multimedia and animation formats
- SWF – could be considered free as of 2009? but needs to be generatable and playable with free tools – declined in phab:T28269
- Форматы шрифтов
- OpenType или Open Font Format
Несвободные форматы файлов
Requested at least once, via automatic conversion of these formats to a free format on upload.
- Sound formats: WMA, RA – phab:T45149
- Video formats: WMV, RM, FLV – phab:T45150
- Microsoft Office formats: DOC, XLS, PPT – phab:T45154
Most of the above issues are tracked as “Multimedia and file format support” issues in phab:T44725.
Альтернативные варианты поддержки
You may upload source materials for files uploaded to Commons (such as camera raw files and bigger FLAC audio) to Internet Archive and linked it in Commons.[Note 9]
Примечания
- ↑ Мегапиксель (количество кадров × ширина × высота), формула понижение разрешения (для ограничения WikiMedia сохраните соотношение сторон): целая часть (√Мегапиксель limit × ширина ÷ высота) ≥ ширинановая, для анимации (кроме того, с потерей SAR): целая часть (Ограничение по мегапикселям ÷ кол-во кадров ÷ высота) ≥ ширинановая
- ↑ Некоторые данные PNG отображаются в MediaWiki в разделе «метаданных»: например, разрешение
pHYs, временная меткаtIMEи другие текстовые данные (комментарии). Но прм этом они не являются данными EXIF. MediaWiki отображает все данные XMP в PNG-файлах, которые поддерживают все те же поля, что и EXIF. - ↑ For JPEG also see A few scanning tips, scantips.com, 2010 by Wayne Fulton.
- ↑ a b c Our Ogg convention differs from the upstream Xiph convention in that we only care about differentiating audio
.ogafrom video.ogv. The Xiph.Org Foundation recommends using.oggas the extension for Ogg Vorbis audio files,.ogafor Ogg FLAC audio,.ogvfor Ogg Theora video, and.opusfor Ogg Opus audio per RFC 5334 and RFC 7845. See also MIME Types and File Extensions - XiphWiki. - ↑ See Opus Recommended Settings.
- ↑ See MDN page: Web video codec guide. See Can I use webm, av1, and ogv. You will find Safari lagging behind, but that is what transcoding is for.
- ↑ For JPEG2000 some developers have been concerned about submarine patents (LoC digitalpreservation), and in 2009 Mozilla tagged it as WONTFIX.
- ↑ Decoding of JPEG 2000 images in PDFs is fully supported, so uploaders of PDF files need not worry about the format being unsupported in this use case
- ↑ Previously there is an unofficial companion website that accepts all file formats named Commons Archive; it is no longer online. There is a back up of files previously existed there in Internet Archive.
См. также
- Commons:Chart and graph resources
- Category:Commons resources – resources, help, tools, links, FAQs, labs, software, etc.
- Commons:Первые шаги/Качество и описание
- Commons:Graphic Lab – helps improve all graphical content
- Commons:Map resources
- Викисклад:Медиапомощь: Help for how to play and create media files.
- Commons:MIME type statistics
- Commons:Рамки проекта/Типы файлов
- Викисклад:Программное обеспечение: If you need help with viewing or creating these formats, please see the useful software.
- Help:Converting video: Help for converting video format.
- Help:Creating a DjVu file/ru
- Справка:Сканирование
- Manual:Adding support for new filetypes
- Category overviews (category trees): Commons:File types/category tree
- On English Wikipedia