Beskrywing
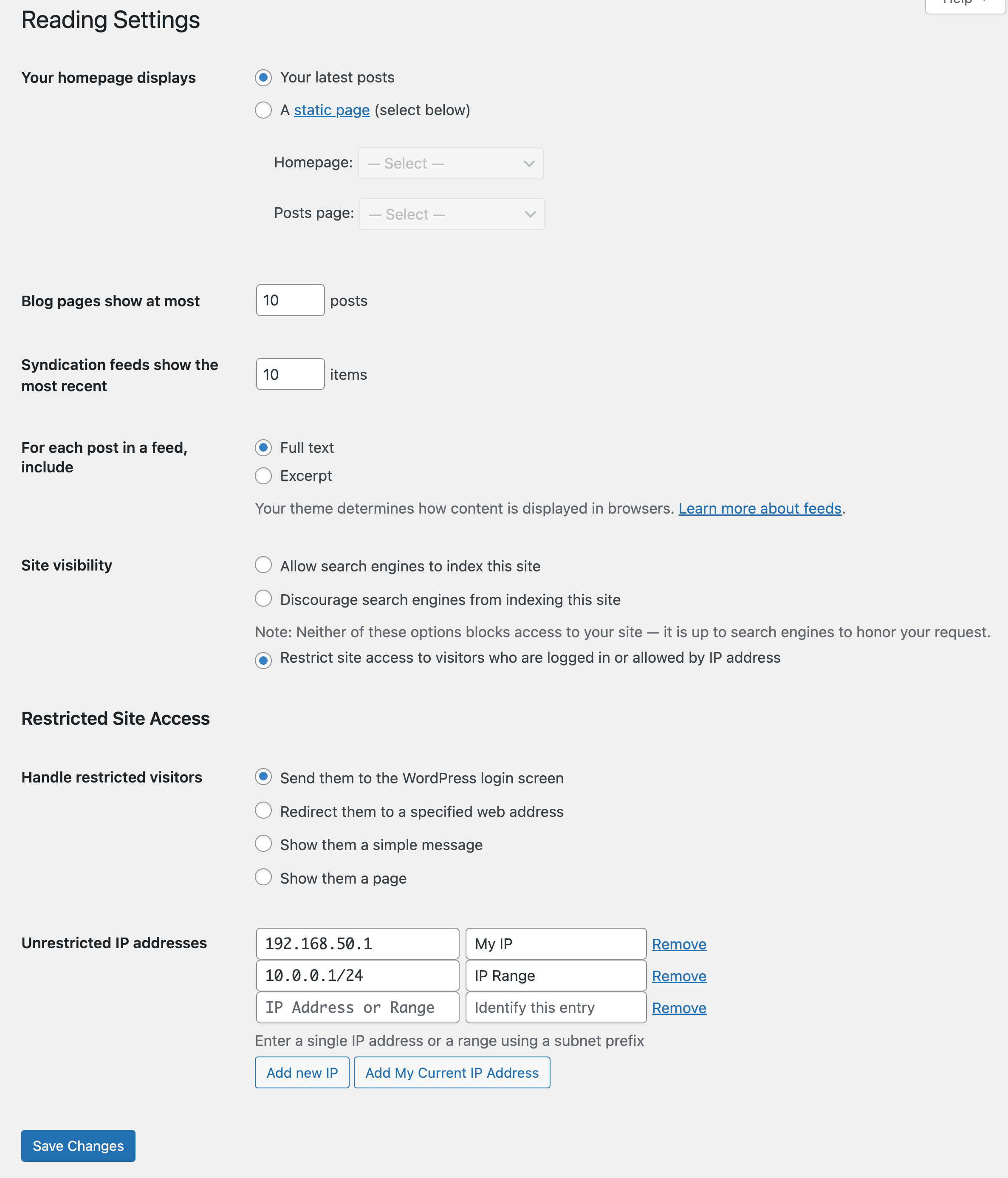
Limit access your site to visitors who are logged in or accessing the site from a set of specified IP addresses. Send restricted visitors to the log in page, redirect them, or display a message or page. A great solution for Extranets, publicly hosted Intranets, or parallel development / staging sites.
Adds a number of new configuration options to the Reading settings panel as well as the Network Settings panel in multisite. From these panels you can:
- Enable or disable site restriction
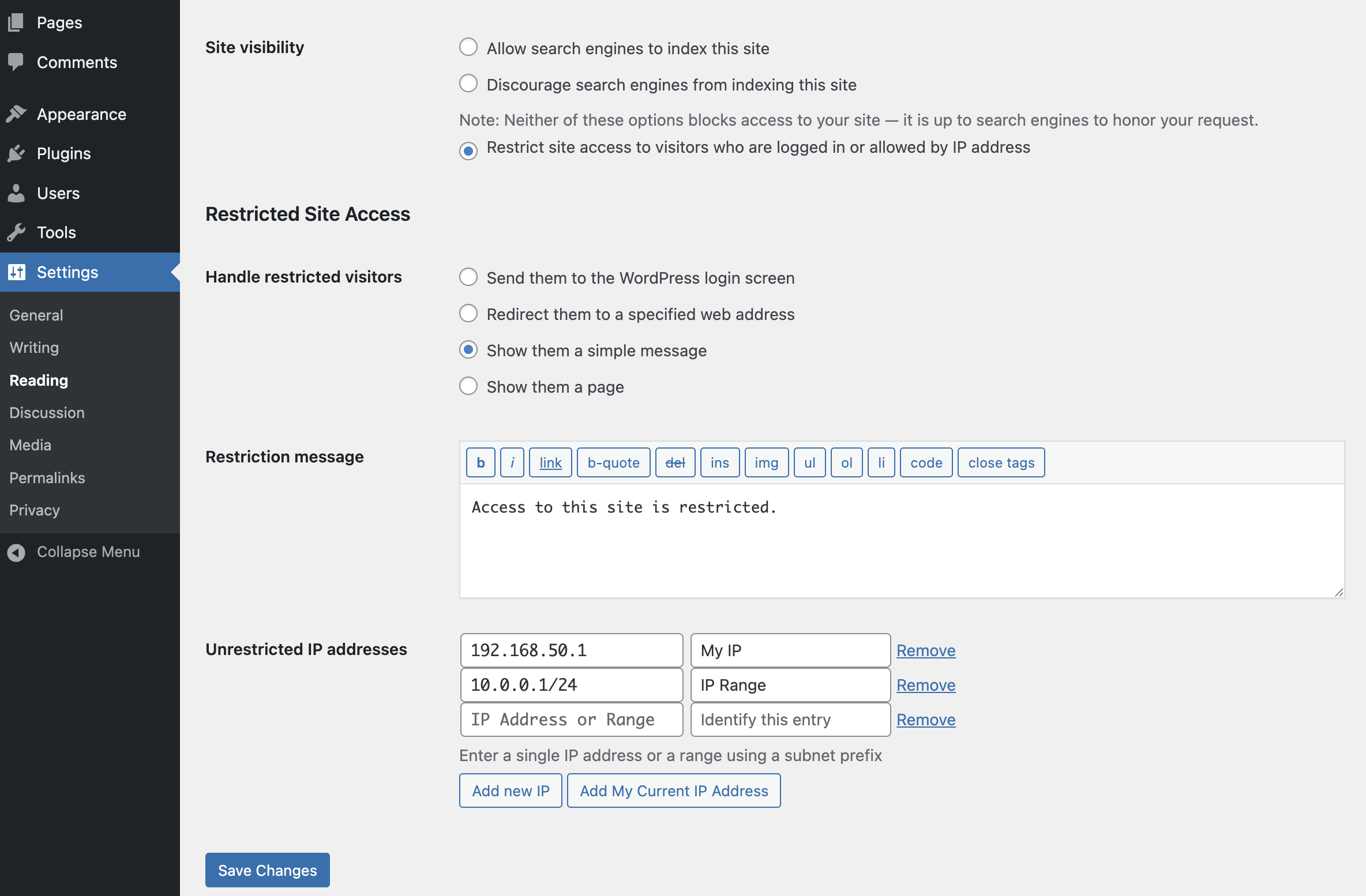
- Change the restriction behavior: send to login, redirect, display a message, display a page
- Add IP addresses to an unrestricted list, including ranges
- Quickly add your current IP to the unrestricted list
- Customize the redirect location, including an option to send them to the same requested path and set the HTTP status code for SEO friendliness
- Define a simple message to show restricted visitors, or select a page to show them – great for “coming soon” teasers!
Screenshots
Installation
- Install easily with the WordPress plugin control panel or manually download the plugin and upload the extracted folder to the
/wp-content/plugins/directory. - Activate the plugin through the ‘Plugins’ menu in WordPress.
- Configure the plugin by going to the “Reading” menu (WP3.5+) or “Privacy” (earlier versions) under “Settings”.
Kwel-vrae
-
Where do I change the restriction settings?
-
Restricted Site Access settings are added to the Reading page, with WordPress’s built in site privacy options. (It was moved there from a separate Privacy settings page in 3.5.)
-
It’s not working! My site is wide open!
-
Most commonly, Restricted Site Access is not compatible with some page caching solutions. While the plugin hooks in as early as it can to check visitor permissions, its important to understand that some page caching plugins generate static output that prevents plugins like Restricted Site Access from ever checking individual visitors.
To the extent that sites blocked by this plugin should not need to concern themselves with high scale front end performance, we strongly recommend disabling any page caching solutions while restricting access to your site. Keep in mind that most page caching plugins do not cache the “logged in” experience, anyhow. Also note that the plugin is fully compatible with other caching layers, like the WordPress object cache.
-
How do I allow access to specific pages or parts of my site?
-
Developers can use the
restricted_site_access_is_restrictedfilter to override normal restriction behavior. Note that restriction checks happen before WordPress executes any queries; it passes the query request from the global$wpvariable so developers can investigate what the visitor is trying to load.For instance, to unblock an RSS feed, place the following PHP code in the theme’s functions.php file or in a simple plug-in:
add_filter( 'restricted_site_access_is_restricted', 'my_rsa_feed_override', 10, 2 ); function my_rsa_feed_override( $is_restricted, $wp ) { // check query variables to see if this is the feed if ( ! empty( $wp->query_vars['feed'] ) ) { $is_restricted = false; } return $is_restricted; } -
How secure is this plug-in?
-
Visitors that are not logged in or allowed by IP address will not be able to browse your site (though be cautious of page caching plugin incompatibilities, mentioned above). Restricted Site Access does not block access to your “real” files, so direct links to files in your media and uploads folder (for instance) are not blocked. It is also important to remember that IP addresses can be spoofed. Because Restricted Site Access runs as a plug-in, it is subject to any other vulnerabilities present on your site.
Restricted Site Access is not meant to be a top secret data safe, but simply a reliable and convenient way to handle unwanted visitors.
In 7.3.2, two new filters were added that can be utilized to help prevent IP spoofing attacks. The first filter allows you to set up a list of approved proxy IP addresses and the second allows you to set up a list of approved HTTP headers. For any sites that were using Restricted Site Access prior to version 7.5.0, a handful of HTTP headers are trusted by default. To change this, utilize the
rsa_trusted_headersfilter to modify the HTTP headers you want to trust. If your site is not running behind a proxy, we recommend doing the following:add_filter( 'rsa_trusted_headers', '__return_empty_array' );This will then only use the
REMOTE_ADDRHTTP header to determine the IP address of the visitor. This header can’t be spoofed, so this will increase security. Note that this is now the default for all new installs since version 7.5.0.If your site is running behind a proxy (like a CDN), you usually can’t rely on the
REMOTE_ADDRHTTP header, as this will contain the IP address of the proxy, not the user. If your proxy uses static IP addresses, we recommend using thersa_trusted_proxiesfilter to set those trusted IP addresses:add_filter( 'rsa_trusted_proxies', 'my_rsa_trusted_proxies' ); function my_rsa_trusted_proxies( $trusted_proxies = array() ) { // Set one or more trusted proxy IP addresses. $proxy_ips = array( '10.0.0.0/24', '10.0.0.0/32', ); $trusted_proxies = array_merge( $trusted_proxies, $proxy_ips ); return array_unique( $trusted_proxies ); }And then use the
rsa_trusted_headersfilter to set which HTTP headers you want to trust. Consult with your proxy provider to determine which header(s) they use to hold the original client IP:add_filter( 'rsa_trusted_headers', 'my_rsa_trusted_headers' ); function my_rsa_trusted_headers( $trusted_headers = array() ) { // Set one or more trusted HTTP headers. $headers = array( 'HTTP_X_FORWARDED', 'HTTP_FORWARDED', ); return $headers; }If your proxy does not use static IP addresses, you can still utilize the
rsa_trusted_headersfilter to change which HTTP headers you want to trust. -
I received a warning about page caching. What does it mean?
-
As of version 7.6.0, RSA attempts to prevent full page caching on sites with an IP address allow list. This is to prevent the page content from being stored at the caching level and displayed to unauthorized visitors.
Page caching plugins often hook into WordPress to quickly serve the last cached output of a page before we can check to see if a visitor’s access should be restricted. Not all page caching plugins behave the same way, but several solutions – including external solutions we might not detect – can ignore the no-caching headers set by WordPress and show cached content to unauthorized users.
-
Why can’t logged-in users see all the sites on my multisite instance?
-
In 6.2.0, the behavior in a multisite install changed from allowing any logged-in user to see a site to checking their role for that specific site. This is a safer default given the varying ways multisite is used; however, if you would prefer to rely on the previous behavior rather than explicitly adding users to each site, place the following PHP code in the theme’s functions.php file or in a simple plug-in:
add_filter( 'restricted_site_access_user_can_access', 'my_rsa_user_can_access' ); function my_rsa_user_can_access( $access ) { if ( is_user_logged_in() ) { return true; } return $access; } -
Is there a way to configure this with [WP-CLI](https://make.wordpress.org/cli/)?
-
As of version 7.0.0, CLI integration has been added. To see the available commands, type the following in your WordPress directory:
$ wp rsa -
How can I programatically define whitelisted IPs?
-
In 7.0.0, the capacity to define a pipe delimited array of whitelisted IP addresses via constant was introduced.
In your
wp-config.phpfile, you can define the following:define( 'RSA_IP_WHITELIST', '192.0.0.1|192.0.0.10' );In 7.1.1, the capacity to programmatically add / remove / set access IPs programmatically was introduced.
The following are valid statements:
Set IPs, ignoring all stored values (but not the constant defined values), if you’re going to use the approach with array indices rather than mixing the two.
Restricted_Site_Access::set_ips( array( '192.168.0.1', '192.168.0.2', '192.168.0.3' ) ); Restricted_Site_Access::set_ips( array( 'labelfoo' => '192.168.0.1', 'labelbar' => 192.168.0.2', 'labelbaz' => 192.168.0.3' ) );Add IPs, if they’re not already added.
Restricted_Site_Access::append_ips( array( '192.168.1.5' => 'five', '192.168.1.6' => 'six' ) );Remove IPs, if they are in the list.
Restricted_Site_Access::remove_ips( array( '192.168.1.2','192.168.1.5','192.168.1.6', ) ); -
Is there a constant I can set to ensure my site is (or is not) restricted?
-
As of version 7.1.0, two constants were introduced that give you the ability to specify if the site should be in restricted mode.
You can force the plugin to be in restricted mode by adding the following to your
wp-config.phpfile:define( 'RSA_FORCE_RESTRICTION', true );Or to ensure your site won’t be in restricted mode:
define( 'RSA_FORBID_RESTRICTION', true );Make sure you add it before the
/* That's all, stop editing! Happy blogging. */line.Please note that setting
RSA_FORCE_RESTRICTIONwill overrideRSA_FORBID_RESTRICTIONif both are set. -
What does ‘Discourage search engines from indexing this site’ do?
-
When the ‘Discourage search engines from indexing this site’ option is enabled, it prevents search engines from indexing the site while still permitting access to regular visitors.
-
What does ‘Restrict site access to visitors who are logged in or allowed by IP address’ do?
-
When this option is activated, it serves as a barrier to all visitors except those who are authenticated (logged in) or whose IP addresses are included in the ‘Unrestricted IP addresses’ setting. This restriction applies universally, even to automated crawlers such as search engines.
Aanbevelings
Contributors & Developers
“Restricted Site Access” is oopbron sagteware. Die volgende mense het bygedra tot die ontwikkeling van hierdie uitbreiding:
Contributors“Restricted Site Access” has been translated into 6 locales. Thank you to the translators for their contributions.
Translate “Restricted Site Access” into your language.
Interested in development?
Browse the code, check out the SVN repository, or subscribe to the development log by RSS.
Changelog
7.6.1 – 2025-10-29
- Fixed: Ensure field data is set properly before we use it. Resolves a fatal error with Elementor (props @ktorktor, Vishal Patel, fatjester, @dkotter, @peterwilsoncc via #371).
7.6.0 – 2025-10-27
- Added: New setting allowing you to hide the WordPress admin bar on the frontend for specific user roles (props @sanketio, @fabiankaegy, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #362).
- Added: New
RSA_NETWORK_MODEconstant to define default setting for network mode for multisite (props @sanketio, @claytoncollie, @dkotter via #363). - Added: More details on how caching may impact the plugin (props @peterwilsoncc, @jakemgold, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via GHSA-jfqv-gvp2-qq5f).
- Fixed: Ensure IP addresses can be saved properly at the network level (props @dkotter, @peterwilsoncc via #367).
- Security: Prevent caching of page content when using an IP allow list (props @peterwilsoncc, @fabiankaegy, @joemcgill, @jakemgold, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via GHSA-jfqv-gvp2-qq5f).
- Security: Bump
cross-spawnfrom 7.0.3 to 7.0.6,@wordpress/scriptsfrom 29.0.0 to 30.16.0 andhttp-proxy-middlewarefrom 2.0.6 to 2.0.9 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #355). - Security: Bump
tar-fsfrom 3.0.8 to 3.0.9 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #359). - Security: Bump
brace-expansionfrom 1.1.11 to 1.1.12,on-headersfrom 1.0.2 to 1.1.0 andcompressionfrom 1.7.4 to 1.8.1 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #361).
7.5.3 – 2025-05-19
Note that this version bumps the WordPress minimum supported version from 6.5 to 6.6.
- Changed: Bump WordPress “tested up to” version 6.8 (props @kmgalanakis, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #349, #352).
- Changed: Bump WordPress minimum from 6.5 to 6.6 (props @jeffpaul via #351, #352).
- Fixed: PHP Notice that the function
_load_textdomain_just_in_timewas called incorrectly (props @kmgalanakis, @dkotter via #350). - Security: Bump
axiosfrom 1.7.4 to 1.8.3 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #346).
7.5.2 – 2025-02-05
Note that this version bumps the WordPress minimum supported version from 6.4 to 6.5.
- Changed: Bump WordPress “tested up to” version 6.7 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @mehidi258 via #335, #336).
- Changed: Bump WordPress minimum from 6.4 to 6.5 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @mehidi258 via #335, #336).
- Fixed: Add missing textdomain to a few strings (props @NekoJonez, @dkotter via #338).
- Security: Bump
axiosfrom 1.6.7 to 1.7.4 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #326). - Security: Bump
webpackfrom 5.90.0 to 5.94.0 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #327). - Security: Bump
wsfrom 7.5.10 to 8.18.0 and@wordpress/scriptsfrom 27.1.0 to 29.0.0 (props @dependabot, @faisal-alvi via #328). - Security: Bump
expressfrom 4.19.2 to 4.21.2,sendfrom 0.18.0 to 0.19.0 andserve-staticfrom 1.15.0 to 1.16.2 (props @dependabot, @peterwilsoncc via #340). - Security: Bump
@wordpress/e2e-test-utils-playwrightfrom 1.7.0 to 1.16.0,nanoidfrom 3.3.7 to 3.3.8,mochafrom 10.2.0 to 11.0.1 and removescookie(props @dependabot, @peterwilsoncc via #341).
7.5.1 – 2024-07-09
Note that this version bumps the WordPress minimum supported version from 5.7 to 6.4.
- Changed: Bump WordPress “tested up to” version 6.6 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #313, #318).
- Changed: Bump WordPress minimum from 5.7 to 6.4 (props @sudip-md, @jeffpaul, @dkotter via #313, #318).
- Security: Bump
tj-actions/changed-filesfrom 32 to 41 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #297). - Security: Bump
expressfrom 4.18.2 to 4.19.2 (props @dependabot, @Sidsector9 via #312). - Security: Bump
follow-redirectsfrom 1.15.5 to 1.15.6 (props @dependabot, @Sidsector9 via #312). - Security: Bump
webpack-dev-middlewarefrom 5.3.3 to 5.3.4 (props @dependabot, @Sidsector9 via #312). - Security: Bump
bracesfrom 3.0.2 to 3.0.3 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319). - Security: Bump
pac-resolverfrom 7.0.0 to 7.0.1 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319). - Security: Bump
socksfrom 2.7.1 to 2.8.3 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319). - Security: Bump
wsfrom 7.5.9 to 7.5.10 (props @dependabot, @iamdharmesh via #319).
7.5.0 – 2023-12-14
Note: this release changes the default behavior for new installs in regards to IP detection. This shouldn’t impact existing installs but there are two filters that can be used to change this behavior. See the readme for full details.
- Fixed: Update code snippet in the readme (props @dkotter, @jeffpaul via #291).
- Security: For new installs, ensure we only trust the
REMOTE_ADDRHTTP header by default. Existing installs will still utilize the old list of approved headers but can modify this (and are recommended to) by using thersa_trusted_headersfilter (props @dkotter, @peterwilsoncc, @dustinrue, @mikhail-net, Darius Sveikauskas via #290). - Security: Bump
axiosfrom 0.25.0 to 1.6.2 and@wordpress/scriptsfrom 23.7.2 to 26.19.0 (props @dependabot, @dkotter via #293).